Planetary Conjunction in March: Witness Venus, Mars, and the Crescent Moon in a Night Sky!
5th Mar 2024
Just in a few days, on March 7-8, Venus, Mars, and the Crescent Moon will align in a captivating planetary parade, and you’ll be able to see it! Yes, we’re talking about trion conjunction! What is it, why and when will it happen? Get to know in the article!
WHAT?
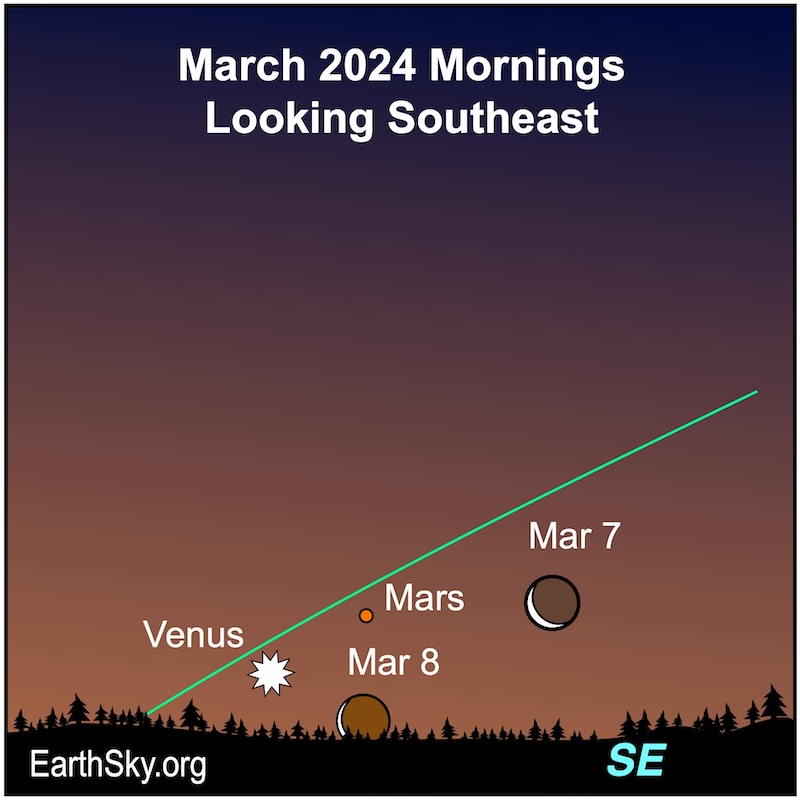
Venus, the most luminous planet, will grace the morning sky in early March, gradually descending amidst the morning twilight with each passing day. At the same time, Mars will steadily ascend. The 4.8%-illuminated Crescent Moon will join the trio. So, on March 7-8, the planets Venus (mag -3.8) and Mars (mag 1.3) will be the brightest dots near the Moon. As the New Moon occurs this week on March 10, the lunar crescent will be thin, but you can still observe it.
Credit: https://earthsky.org
WHEN?
Mars near the Moon
- March 7-8, 04:59 GMT (11:59 p.m. EST)
- Close approach time: 06:51 GMT (1:51 a.m. EST)
- Close approach distance: 3°17′
Venus near the Moon
- March 7-8, 17:01 GMT (12:01 p.m. EST)
- Close approach time: 18:56 GMT (1:56 p.m. EST)
- Close approach distance: 3°00′
WHY?
The answer to this question lies in just one word – “conjunction”. A celestial conjunction takes place when two astronomical objects share the same apparent right ascension or ecliptic longitude in the sky. Simply put, it’s an event where two or more planets appear close together in the sky. In everyday language, the terms “conjunction” and “closest approach” are often used interchangeably. However, it’s crucial to note that conjunction holds a more technical definition and doesn’t occur with every appulse.
Moon-planet conjunctions occur frequently. Once every 27.3 days, our natural satellite passes through a narrow part of the sky centred on the ecliptic and encounters planets. Planetary conjunctions are less frequent.
WHERE?
In the early morning of March 7 and 8, these three celestial objects – Venus, Mars, and the crescent moon – come together to form a triangular pattern near the horizon. If you have binoculars, they can be handy for spotting this trio about 30 to 40 minutes before the sun rises.
As dawn approaches, pay attention to the grouping of Venus, Mars, and the crescent moon in the brightening twilight. Although Mars might be a bit challenging to spot during this level of light, give it a shot using binoculars.
The radiant Venus shines brightly, situated less than 5° above the east-southeast horizon and less than 20° to the lower left of the lunar crescent. For a better view, position Venus at the lower left edge of your binocular field. If the sky is exceptionally clear, you might catch a glimpse of Mars, approximately 6.4° to the upper right near the edge of your visual field.
HOW?
Here are some tips for you to keep in mind for successful observations and spot planets next to the Moon:
- First of all, even if you happen to miss the precise moment of conjunction or closest approach, don’t worry! Whether it’s a little before or after the event, the celestial objects will maintain their proximity, making the observation equally worthwhile.
- The tools you use for observation depend on the angular distance between the objects. Some events may require a telescope, while others can be enjoyed with a good pair of binoculars. Typically, a reliable 10×50 binocular provides a field of view of 6-7°, whereas telescope field of view varies, sometimes less than 1°. You can easily calculate the field of view for your optics. Of course, if you prefer, you can also witness the event with the naked eye.
- Prior to your observation, take a moment to check the weather forecast. The sky should be clear to ensure that clouds won’t disrupt your stargazing.
May your night be filled with wonder and discovery as you gaze upon the sky. Whether you’re a seasoned astronomer or a curious skywatcher, we wish you an amazing stargazing night filled with the magic and mystery of the cosmos. Happy observing!
![Beauty of the Pink Moon And Lyrid Meteor Shower in This Week’s Best Astrophotos [19-26 April] Beauty of the Pink Moon And Lyrid Meteor Shower in This Week’s Best Astrophotos [19-26 April]](https://orbitaltoday.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/Pink-Moon-is-on-its-way-above-the-mountains-1-300x300.jpg)




Thank you for your comment! It will be visible on the site after moderation.