ispace Launching Lunar Relay Data Service for Moon Missions
29th Apr 2024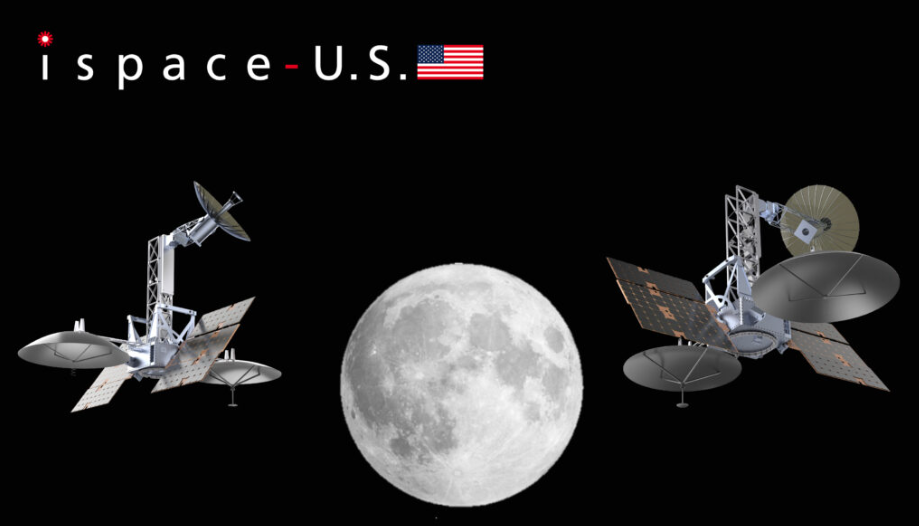
The ispace entity in the U.S. announced on 25th April that it is initiating the ispace lunar relay data service. According to ispace-U.S., the company expects to launch two lunar orbit relay satellites in 2026 as part of Mission 3, which is planned for 2026.
In a press release, ispace-U.S. stated that the satellites will support the APEX 1.0 lunar lander currently planned to to land on the far side of the Moon in Schrödinger Basin near the lunar south pole. The lander will deploy the lunar relay satellites before landing. The satellites will then facilitate data communications between the lander and Earth.
After APEX 1.0 concludes its mission, the satellites will move to a High Circular Polar Orbit and provide a connection between the southern pole of the Moon and Earth more than 70% of the time. The satellites ae expected to operate for several years and provide data communications for other missions. Because the lunar South Pole is of particular interest to space agencies because of the water found in the area, the satellites’ orbits will be designed so that they loiter over the high-latitude southern region.
Building lunar infrastructure
The launch of the infrastructure that will enable clients’ hardware on the Moon to communicate with Earth along with the vehicle that gets them there is an example of how ispace envisions the development of the embryonic lunar economy. The U.S.-led Artemis missions, for example, will be focused there. However, UK based ispace Senior Business Development & Strategy Advisor Jenna Tiwana told Orbital Today that the company sees more than supporting Artemis in its future “… because ispace is really trying to do things commercially. We are trying to establish these commercial value chains on the Moon that will be sustainable. We aren’t going there for a short amount of time, only funded by government.”

![Beauty of the Pink Moon And Lyrid Meteor Shower in This Week’s Best Astrophotos [19-26 April] Beauty of the Pink Moon And Lyrid Meteor Shower in This Week’s Best Astrophotos [19-26 April]](https://orbitaltoday.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/Pink-Moon-is-on-its-way-above-the-mountains-1-300x300.jpg)



Thank you for your comment! It will be visible on the site after moderation.