Ranking: The Most Environmentally Sustainable UK Space Companies
15th Jan 2024
In the previous century, space exploration primarily unfolded as a race among nations, driven by state actors and the fierce competition for supremacy in cosmic endeavours. Technological progress was the province of governments, and their ecological and space arms rarely met, if ever. Fast forward to today, and a paradigm shift is evident. The idea of a ranking of sustainable UK space companies nowadays encompasses a much broader range of companies than ever.
Space exploration is no longer the sole dominion of governmental entities; instead, private companies often lead the way. Technological advancements are now catalyzed by the innovative spirit of individual entrepreneurs and burgeoning startups. In this New Space era, it is the entrepreneur, not the government, who often steers the course of technological development.
This transformation has given rise to a competitive landscape for sustainable UK space companies where they vie for prominence in the space industry. The dynamics have transitioned from geopolitical rivalries to market-oriented competitions, ushering in a new era of space exploration characterized by entrepreneurial vision and market forces.
What is the role of sustainable space tech?
The exploration of space, with a focus on sustainability, stands as a distinctive hallmark of the contemporary space age and the evolving global landscape. Sustainable UK space companies play important roles in several aspects of this change.
Both traditional space exploration and the new space era already have environmental consequences, such as the increasing congestion of Earth’s orbit due to the growing number of satellites. The increase in satellite launches leads to orbital debris, creating challenges for spacecraft navigation and potentially elevating the risk of collisions. Broken satellites that stay in orbit further contribute to this growing space junk problem. Additionally, the amount of space missions grows.
Military defence programs in space are on the rise as well. The militarization of space reflects the evolving geopolitical landscape and the recognition of space as a contested frontier for strategic advantage. Thus, in 2021, the International Space Station had to adjust its orbit to avoid a collision with space debris from a Russian anti-satellite experiment. The commercial space companies contributing to space debris are, however, developing plans to address the issue.
Sustainable practices, like the development of reusable launch vehicles and responsible satellite disposal methods, contribute to preventing space debris and ensuring that exploration efforts do not contribute to long-term environmental degradation. Notably, private companies actively integrate sustainable technologies into their space activities. Plenty of startups are dedicated to developing and implementing sustainable practices within the space industry. Along with sustainable UK space companies, others are focused on working to maintain the space environment.
As such, we have decided to look into which British space companies are incorporating environmental measures into their core products. In this ranking, we don’t include companies that offer environmental solutions as their main commercial offerings. So, without further ado, sustainable UK space companies, in order of their ecologically friendly initiative’s starting date:
| Company | Founding date | Initiative | Initiative started | Benefit |
| Reaction Engines | 1989 | SABRE technology | Since 1989 | The technology enhances the reuse of heat: less energy is wasted, leading to lower overall energy consumption. This contributes to net zero. |
| Orbex | 2015 | Reusable rocket Prime | 2018 | The approach has a transformative effect on the carbon footprint and lifecycle impact of the Orbex launch vehicle. |
| Newton Launch Systems | 2011 | Green propulsion for satellites | 2018 | Green propulsion typically involves the use of propellants or technologies that produce fewer harmful byproducts compared to traditional propulsion systems, reducing the overall carbon footprint. |
| Skyrora | 2017 | Conversion of unrecyclable plastic waste into aerospace fuel | 2019 | Using Ecosene aerospace fuel reduces harmful emissions by 70%. The technology allows to convert 401,054 kg of plastic into 60,158 litres of Ecosene rocket fuel. |
| Space Forge | 2018 | Reusable satellite ForgeStar | 2022 | Space Forge reveals a patent-protected design for a reusable and planet-friendly reentry system, targeting a cost-effective and dependable return of satellites to Earth. |
| Open Cosmos | 2015 | Satellites, PLATERO and MANTIS | 2023 | PLATERO is created for environmental monitoring, and is expected to play a crucial role in shaping future policies and strategies for environmental preservation and safeguarding. |
Reaction Engines
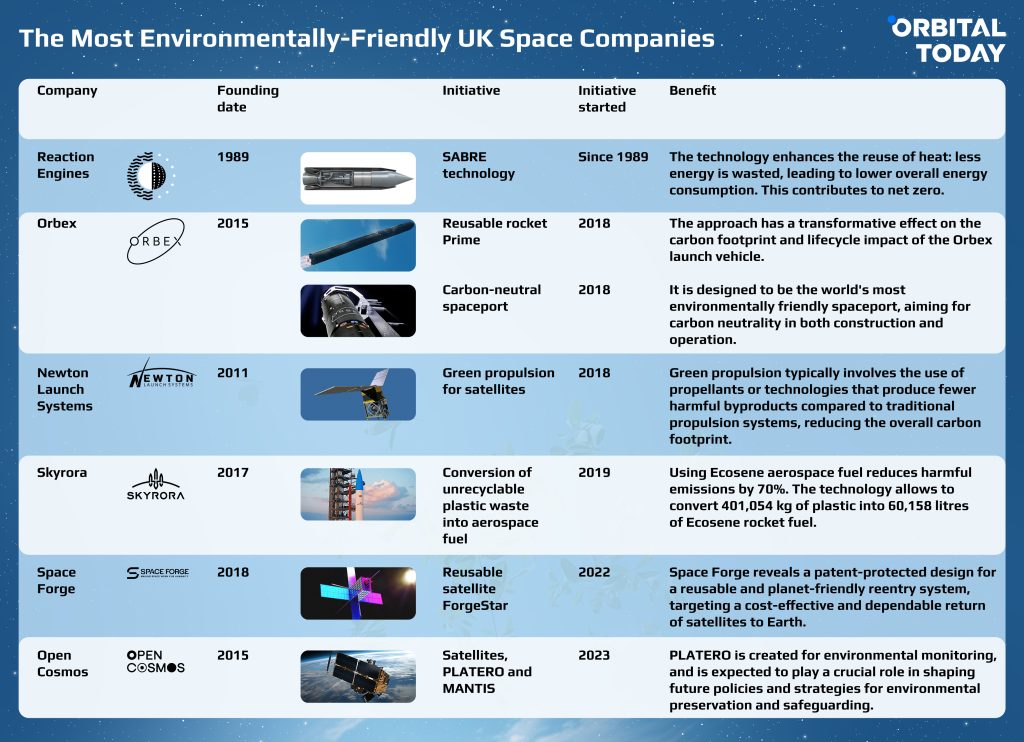
Reaction Engines is at the forefront of aerospace innovation with its focus on designing and developing the Synergetic Air-Breathing Rocket Engine (SABRE), a cutting-edge hypersonic propulsion system.
A major milestone for the company is the breakthrough in aerospace engine technology achieved through the development of ultra-lightweight heat exchangers. These crucial components, integral to the high-speed SABRE engines, mark a significant advancement in thermal management by preventing overheating during high-flight speeds. The potential applications of Reaction Engines’ heat exchanger technology extend across various industries, including aerospace, motorsport, industrial processes, and the energy sector.
The company’s technology extends its impact to address the distinctive heat management challenges inherent in a range of future net-zero systems. These include hybrid-electric, fully electric, hydrogen fuel cell, and hydrogen gas turbine systems, providing solutions to ensure their effective operation in the pursuit of sustainable and emissions-free flight.
In 2016, funding totaling £60 million was secured for the initiative from both the UK government and the European Space Agency (ESA). It was aimed at backing a comprehensive demonstrator cycle. Following this, an extra £3.9 million was granted by the UK Space Agency in July 2021 to support ongoing development efforts.
The company’s contribution to achieving net-zero goals also lies in its technology that enhances the management and reuse of heat. This means that less energy is wasted, leading to lower overall energy consumption. The innovation also aids in the decarbonization of existing energy-intensive sources. Furthermore, it plays a facilitating role in enabling solutions such as Carbon Capture, Utilisation, and Storage (CCUS). CCUS involves capturing carbon dioxide emissions from industrial processes or power plants and either utilising it or safely storing it underground. This contributes to reducing the overall carbon footprint of energy-intensive activities.
Image Credit: Reaction Engines’ website
Orbex
Orbex, an orbital launch services company with UK and Continental offices, is dedicated to catering to the requirements of the small satellite industry. Demonstrating commitment to the European Space Agency’s (ESA) Clean Space initiative, Orbex is engaged in developing what is anticipated to be one of the most environmentally friendly space launch vehicles ever constructed. The company hit a lot of turbulence in 2023, but the installation of a new CEO in 2024 might move these endeavours forward.
The company’s approach to minimizing environmental impact should have a transformative effect on the carbon footprint and lifecycle impact of the Orbex launch vehicle. Positioned as a trailblazer, Prime, Orbex’s creation, is poised to usher in a new era of ultra-green launch systems. The rocket is engineered to be reusable. Upon re-entry to Earth, anything that doesn’t burn up harmlessly in the atmosphere will be recovered and repurposed for subsequent launches. Also, to prevent space debris, the design philosophy behind the Orbex Prime rocket prioritizes a zero-debris approach.
Orbex Prime is fueled by BioLPG, a notable departure from conventional rocket fuels. The Greenhouse Gas (GHG) factor associated with BioLPG is a remarkable 90% lower compared to fossil-based fuels like RP-1, the extensively refined form of Kerosene commonly employed as rocket fuel.
Finally, Sutherland Spaceport, Orbex’s home launch site, is designed to be the world’s most environmentally friendly spaceport, aiming for carbon neutrality in both construction and operation.

Image Credit: Orbex’s website
Newton Launch Systems
Newton Launch Systems, committed to enhancing rocket propulsion for small spacecraft, has actively contributed to sustainable space technology for over a decade. Additionally, the company is now working on establishing a distinctive testing environment. This facility, located at their operational base in Gwynedd, is dedicated to evaluating space and aerospace systems. This environment will include equipment for assessing the performance, reliability, and safety of spacecraft, satellites, propulsion systems, communication systems, and other aerospace technologies.
Recent accomplishments include successful projects, supported by the UK government, focused on implementing green propulsion in satellites. Traditional rocket propellants often release pollutants into the atmosphere, contributing to air pollution and potentially harming ecosystems. Green propulsion typically involves the use of propellants or technologies that produce fewer harmful byproducts compared to traditional propulsion systems, reducing the overall carbon footprint. Additionally, green propulsion systems, which include technologies like electric propulsion, can potentially reduce the creation of space debris.
Another milestone involves the development of a cost-effective bi-propellant rocket engine utilizing standard engineering materials. This approach minimizes the demand for specialized resources and materials that might have a higher environmental impact. Besides, it contributes to minimizing waste during both the manufacturing and operational phases of the rocket engine’s life cycle.
Image Credit: NASA’s website
Skyrora
Edinburgh-based Skyrora specializes in rocket design and production, facilitating access to space for small satellite manufacturers. Their sustainability efforts include a focus on converting unrecyclable plastic waste into Ecosene, an aerospace fuel. Using catalytic pyrolysis, the process reduces harmful emissions by 70%. Skyrora’s Ecosene rocket fuel technology uses catalytic pyrolysis and hydrotreatment to convert plastics including polypropylene (PP), polyester (PE), and polystyrene (PS), with which polystyrene is found to have the best plastic-to-pyrolysis conversion rate. Impressively, their technology allows them to convert 401,054 kg of plastic into 60,158 litres of Ecosene rocket fuel.
Also, Skyrora’s ongoing research explores recycling technologies for diverse plastic waste, including unconventional items like metallized packaging and plastics impacted by UV rays or saltwater.
Skyrora also boasts the largest hybrid 3D printer in Europe, known as SkyPrint2. With the capacity to craft rocket engine parts up to 2.3m in length, SkyPrint2 not only streamlines the intricacies, costs, and time associated with rocket engine development but also fosters a more sustainable manufacturing process. These sustainable production methods are poised to slash carbon emissions by eliminating the need for material transportation.
In further strides towards sustainability, Skyrora is actively developing a range of environmentally conscious space technologies to play a role in achieving ‘Net Zero Space.’ This initiative aims not only to advance space exploration but also to maximize the social and economic benefits of achieving a net-zero impact on Earth.
Image Credit: Skyrora’s website
Space Forge
Space Forge is an aerospace manufacturing company based in Cardiff, Wales. The company’s primary focus is on developing reusable on-orbit fabrication capabilities. Space Forge reveals a patent-protected design for a reusable and planet-friendly reentry system, targeting a cost-effective and dependable return of satellites to Earth. It innovatively leverages space for manufacturing supermaterials, though the current limitations in price and complexity hinder the production range of materials achievable on Earth.
Space Forge’s efforts toward sustainability cover the Pridwen heat shield, employing a large, high-temperature alloy for fully reusable re-entry. The shield’s size surpasses that of the vehicle, utilizing a folding mechanism inspired by origami to fit inside the launcher, marking a significant advance in space technology.
Additionally, the company unveils “Fielder,” an innovative water-based hover net. This uncrewed, agile water vehicle is crafted to position itself beneath re-entry vehicles, softening landings, and ensuring a swift return to a designated port. The introduction of Fielder enhances the reliability and efficiency of the re-entry vehicle return process.
The company is integrating the Pridwen and Fielder technologies into a reusable satellite platform, resulting in the creation of a pioneering in-orbit and return-to-Earth manufacturing service called ForgeStar. This groundbreaking service, deployable from conventional launchers, aims to offer rapid, reliable, and reusable in-space infrastructure. Thus, the ForgeStar initiative represents a significant step forward in the development of sustainable and reusable space technologies.

Image Credit: The Engineer
Open Cosmos
Open Cosmos is a company engaged in the comprehensive lifecycle of advanced satellites, covering design, construction, launch, and operation through their OpenOrbit end-to-end mission management service.
OpenConstellation, a mutualized satellite infrastructure, has been designed to empower organizations to collectively share data generated by satellites, leading to enhanced access to valuable information about our planet. The utilization of this shared capacity serves to reduce overall costs while simultaneously increasing access to higher-quality, more frequent data.
As a part of the sustainable investiGATION OF sPACE, Open Cosmos has successfully launched a new satellite, PLATERO, marking a pivotal step in its OpenConstellation project. This satellite is poised to transform environmental monitoring, offering valuable insights to organizations and businesses globally.
PLATERO is a groundbreaking satellite that integrates Earth Observation (EO), the Internet of Things (IoT), and Artificial Intelligence (AI) onboard processing. Its primary objective is to monitor and analyze various environmental aspects, including biodiversity, desertification, emergencies like wildfires or floods, and the impact of farming practices on the territory. Equipped with a high-performance multispectral camera and IoT capabilities, PLATERO enables real-time, ground-based sensor communication, streamlining decision-making. The data collected by PLATERO is expected to play a crucial role in shaping future policies and strategies for environmental preservation and safeguarding.

Image Credit: TS2
What’s behind our ranking?
The data presented in this ranking is sourced from publicly available information. Recognizing that companies are in various stages of development, we continually monitor their activities for an objective assessment. This is an ongoing effort, specifically centred on UK industry players.
Notably, companies primarily engaged in sustainability as commerce are not concluded in this version of the rating. Our ranking of sustainable UK space companies will no doubt have a companion piece that looks precisely at this aspect of the market.





Thank you for your comment! It will be visible on the site after moderation.