ESA ExoMars sees first-ever Martian green glow
16th Nov 2023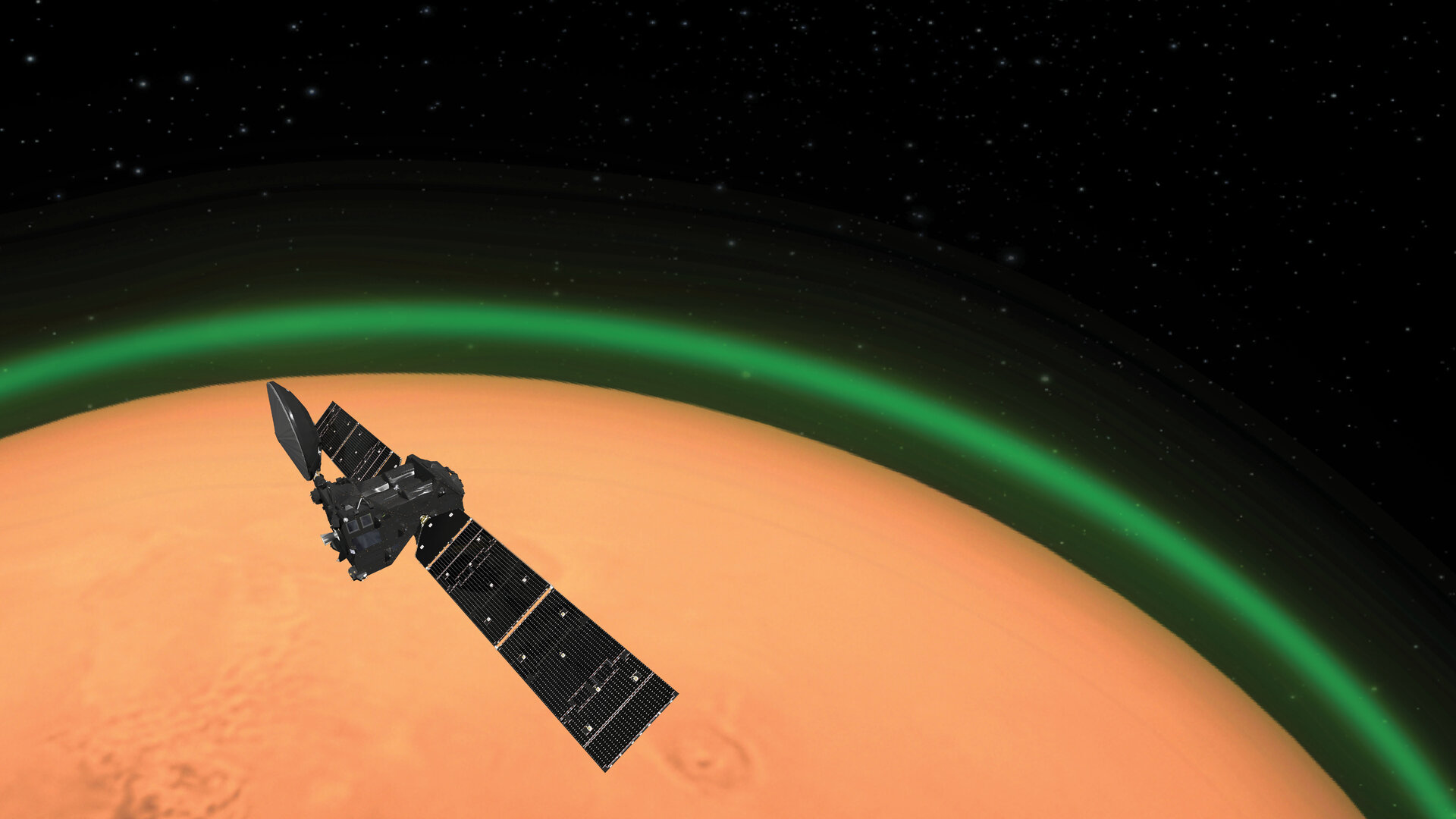
A mysterious green luminescence appeared in the Martian night sky. This phenomenon has been observed for the first time by The European Space Agency’s ExoMars Trace Gas Orbiter (TGO).
The green illumination showed up approximately 50 kilometres above the Martian surface. The TGO also observed air flow in Mars’ atmosphere.
What is the origin of the green Martian night sky?
The green tint in Mars’ atmosphere is indicative of the presence of oxygen. This nightglow phenomenon occurs when two oxygen atoms combine to form an oxygen molecule.
During the daytime on Mars, sunlight interacts with carbon dioxide (CO2) molecules in the planet’s atmosphere. The energy from the Sun prompts the photodissociation or photolysis of carbon dioxide molecules, causing them to split into individual oxygen atoms.
These newly released oxygen atoms then traverse through the Martian atmosphere to the night side. In the absence of solar energy, these oxygen atoms bond together to create oxygen molecules (O2).
As the oxygen molecules transition to a lower energy state during this process, they emit light. This light emission is responsible for the distinct green glow observed in the Martian atmosphere.
Before ExoMars, had we detected this glow?
For many years, scientists have theorized the existence of a captivating airglow on Mars. However, it wasn’t until a few years ago that ESA’s Mars Express orbiter first detected it in the infrared spectrum. In 2020, the TGO captured a similar occurrence in visible light. Although, it occurred during Martian daylight rather than at night.
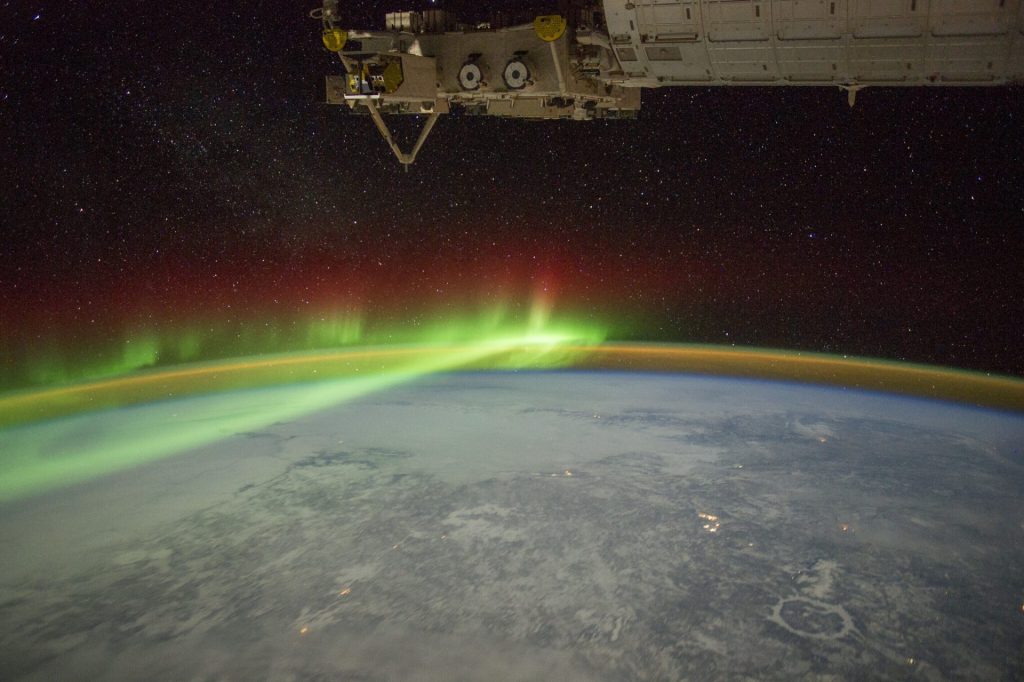

Is the Martian green glow the same as Aurora?
The nightglow should not be confused with auroras. Planetary atmospheres light up not only through auroras but also through nightglow.
Both on Mars and Earth, auroras result from energetic solar electrons interacting with the upper atmosphere, displaying variations. In contrast, nightglow is more consistent and can showcase diverse colours. They are based on the prevalence of different atmospheric gases at varying altitudes.
What is the scientific value of this phenomenon?
The nightglow serves as a valuable indicator for studying atmospheric processes. It can provide valuable information about the composition and dynamics of an atmospheric region that is difficult to measure.
Additionally, it unveils details about oxygen density and the mechanisms through which both sunlight and solar wind deposit energy.
Understanding the parameters of the Martian atmosphere for upcoming space missions
This inherent bright illumination is also crucial for missions targeting Mars’s surface. It could serve as a helpful aid for human visibility and rover navigation amid the darkness of Martian nights.
Additionally, atmospheric density directly influences the drag encountered by orbiting satellites. It affects the effectiveness of parachutes employed in delivering probes to the Martian surface as well.
The scientists suggest that as future astronauts venture into Mars’s polar regions, they will witness a luminous green glow illuminating the Martian night sky.






Thank you for your comment! It will be visible on the site after moderation.