Meteor Shower In The UK 2024: A Space Show You Don’t Want To Miss
15th Apr 2024
This mesmerising spectacle is available to every Briton. Some call it Starfall, but this phenomenon has nothing to do with stars. Today, we will answer the following questions: what is a meteor shower, when is the next meteor shower in the UK, and how to prepare and not miss a single moment of this magic sky show?
What Is A Meteor Shower?
A meteor shower or a Starfall is a phenomenon that creates a beautiful picture in the night sky – myriads of falling stars with short or long luminous tails. It looks like a magnificent, miraculous fireworks display, only from space, especially if you choose the right place for observation. But unlike stars, meteors are burning down in the sky.
What Is A Meteor?
A meteor is a phenomenon that occurs when a minor meteoroid burns upon entering the Earth’s atmosphere. Such meteoroids can be fragments of asteroids, comets, or simply space debris. The term “meteor” comes from a Greek word meaning “floating in the air.” When saying “shooting stars”, people usually mean weak meteors, whereas stronger ones are called fireballs.
From Earth’s surface, we see the path of a burning celestial body as a moving stream of light, scientifically called a meteor trail.
Meteor vs Meteorite: Keep The Differences
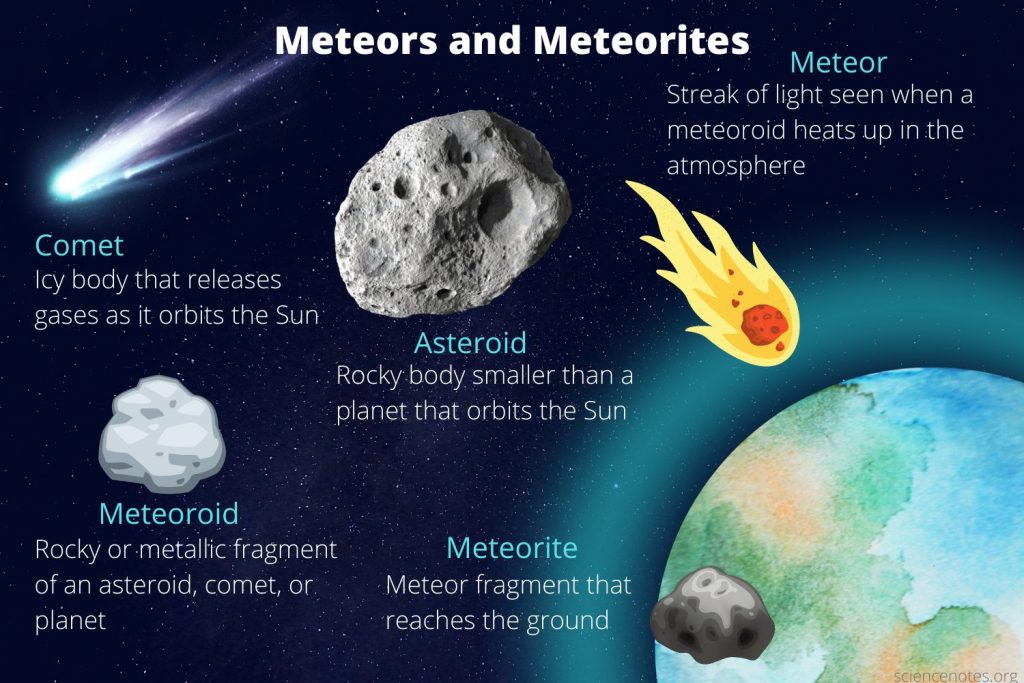
A meteor is often confused with a meteorite, so it is important to distinguish between these two. A meteor is a trace of a celestial body burning in the Earth’s atmosphere, and a meteorite is a stone from space, a fragment of an asteroid that fell to Earth. Accordingly, a meteor shower consists of luminous meteoroids that do not fall to the ground, while a meteorite shower consists of solid meteorites that do fall to the ground.
The phenomenon of a luminous meteoroid trace will always be called a meteor, and it does not matter whether this celestial body burns up in the atmosphere, passes through the atmosphere and returns to outer space, or falls to Earth as a meteorite. You can learn more about the differences in our article Comet Vs Asteroid Vs Meteor: What are they?
How Is A Meteoroid Stream Formed?
One meteoroid that enters the atmosphere and leaves a mark is a meteor. Random meteors are not associated with a meteor shower and can be observed at any time in any location.
When many meteoroids come from a specific comet, the phenomenon is called a meteor shower. How does it arise? In addition to the Earth and other planets, many comets revolve around the Sun in somewhat lopsided orbits. As a comet approaches the Sun, its icy surface begins to evaporate. Many stones and dust particles are released, filling the space along the comet’s path.
There is especially much debris from comets in the inner solar system, since most of the icy surface is exposed to the Sun’s rays. The Earth, revolving around the Sun, crosses the orbit of a comet and, naturally, collides with streams of cometary debris. Numerous stones and dust particles (meteoroids) fly into the Earth’s atmosphere, burn up, and leave a mark as they form streams. And from down here, we see a meteor shower.
What Is A Radiant, And Where Do Meteors Come From?
People who witnessed the meteor shower note that, looking at the sky, it seems as if the stars are falling from one point, forming a kind of dome that is reminiscent of fireworks. Actually, this is not true. Celestial bodies do not fly out from one point. They move in orbit, in parallel and at the same speed, but to us, looking from below, it seems that the meteoroids are coming out from one point because of our perspective. It’s like seeing railroad tracks converge at one point on the horizon. The imaginary point at which shooting stars emerge is called the aurora point or radiant.
Today, in the UK, meteors are assigned the names of those constellations from which they are expected to emerge. For example, the Perseids radiant is in the constellation Perseus, and the Leonids radiant is in the constellation Leo. As the Earth rotates around the Sun and on its axis, the point of aurora slowly moves across the night sky, and to us, it seems that the stars are moving, too. At the moment when the radiant reaches its highest point, we can observe a “starfall”.
Observing meteor showers throughout history
Meteor showers have been observed at all times:
- The first mentions date back to 687 BC in the work of the ancient Chinese “Zuo Zhuan”.
- In the 4th century BC, Greek philosopher Diogenes of Apollonia spoke on the cosmic origin of starfalls.
- In 1091, the ancient Russian Laurentian Chronicle recorded the appearance of a fireball, calling it a heavenly serpent.
- A record of a meteor shower was found in the Timbuktu manuscripts in August 1583.
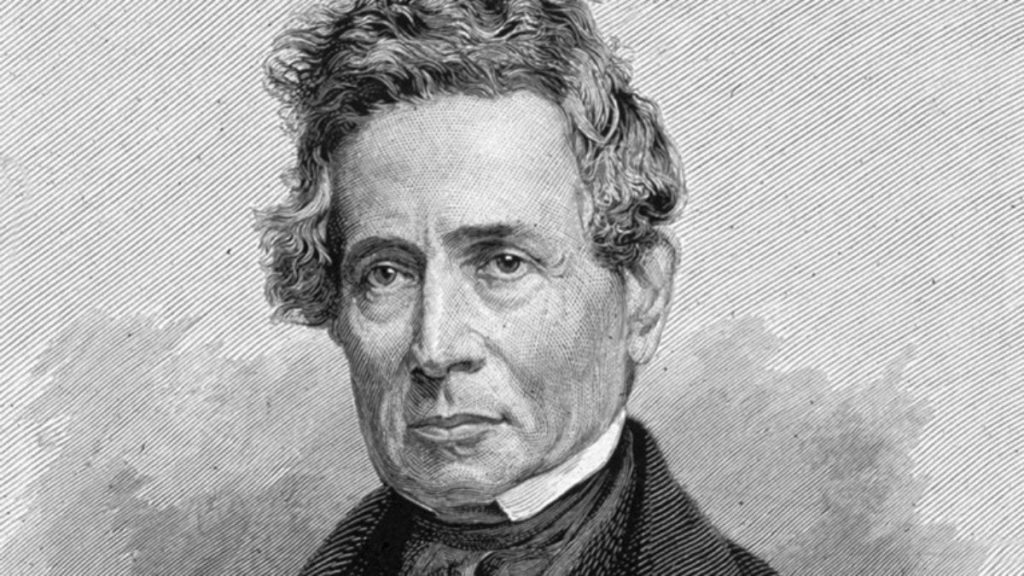

American scientist Denison Olmsted was one of the first to suggest that starfalls are cosmic bodies that enter the Earth’s atmosphere rather than atmospheric phenomena. It was he who observed and studied the famous Leonid meteor shower in 1833 and came to the conclusion that it came from the Leo constellation and was not visible in Europe. However, he could not answer why this happens and why starfalls occur every year.
The answer was found by Italian astronomer Giovanni Schiaparelli. He saw the relationship between comets and starfalls and wrote his Notes and Reflections About the Astronomical Theory of Shooting Stars in 1867.
The study of meteor showers was carried out in all subsequent years, and today there is enough information about the formation of meteor showers. Scientists can say exactly what is the best direction to watch the meteor shower, and how to prepare for it.
How To See A Starfall?
We can observe meteor showers every year on certain days. What is the best time to see the meteor shower in the UK? The maximum number of falling meteors can be seen at night, closer to dawn.
The main thing to keep in mind is that the sky has to be clear, so that the clouds don’t cover the falling stars. The fiery traces of burning celestial bodies that have fallen into the Earth’s atmosphere differ in their glow intensity. Some may be barely noticeable, while others may surprise you with their brightness and variety of colours. To enjoy the meteor shower tonight in the UK, follow the advice of seasoned astronomers.
How To Prepare For A Meteoroid Shower In The UK?
It’s best to observe the starfalls with the naked eye, so forget about buying a telescope or binoculars and follow these simple tips:
- Check, when is the peak of the meteor shower.
- Determine the aurora point in the sky from which meteoriods will emerge.
- Choose an observation spot where the sky is as dark as possible.
- Wait for the meteor shower to kick in on your side of the Earth.
- Your eyes will need about half an hour to adapt to the darkness so that you can see the stars better. Try not to look at your smartphone.
- Try to determine the direction of the meteor shower and the aurora point.
- Enjoy watching the meteor shower for 30 minutes, then rest for a few minutes and continue observing.
- Do not stare at your phone, not to miss the meteoroid flight.
Watching the starfalls will be enjoyable if you are in a safe and comfortable environment. Please note that you will be spending several hours outside, so dress warmly – at any time of the year, even in summer. Bring a lounge chair, recliner, or bean bag. This way, you will eliminate neck stiffness and back pain.
Choose the best place to see meteor shower tonight in UK so that the viewing angle of the sky is 60°. At this location, the atmosphere’s thickness allows seeing the maximum number of meteoroids without reducing the brightness of their trails.
Why Should You Record Your Observations?
Recording your observations is essential if you are a hobby astronomer or want to help British Astronomical Association scientists with their research. You need to write down:
- Observer’s name, surname, and contact details.
- Observation date, indicating the night after which date you observed the stars, as well as what time the meteor showe was seen in the UK.
- The exact coordinates from where the observations were made (latitude and longitude).
- Description of the trail seen, with an estimate of its magnitude, indicating the constellation from which the shower was observed.
- The number of seconds during which the trail was visible.
- Features of the trail, such as colour, explosion, etc.
To know if there’s a meteor shower tonight to observe, bookmark the table below.
Meteor Showers of 2024
There have already been meteor showers in 2024, but if you missed them, stay calm. The Earth will encounter space debris left by comets several more times this year, so you will be able to see this amazing phenomenon. So let’s see, when is the next meteor shower in the UK.
Meteor Showers In March-December 2024
| Name | Date | Peak | Radiant | Parent body (comet) | Moon illumination at its peak |
| Gamma Normids (γ-Normid) | 25 February – 28 March | 14–15 March | Norma | Unknown | 20-30% (view from Sydney, Australia) |
| Lyrids | 14–30 April | 22-23 April | Near Lyra | C/1861 G1 (Thatcher) | 98-99% |
| Pi Puppids | 15-28 April | 23-24 April | Puppis | 26P/Grigg-Skjellerup comet | 99-100% |
| Eta Aquariids | 19 April – 28 May | 6 May | Aquarius | Halley’s Comet | 4% (two days before the new moon) |
| Alpha Capricornids | 3 July – 15 August | 30 July | Capricornus | 169P/NEAT comet | 27% |
| Southern Delta Aquariids | 12 July – 23 August | 30 July | Aquarius | 96P/Machholz comet | 31% (view from Sydney, Australia) |
| Piscis Austrinus | 15 July – 10 August | 28 July | Piscis Austrinus | Unknown | 54% (view from Sydney, Australia) |
| Perseids | 17 July – 24 August | 12–13 August | Perseus | 109P/Swift–Tuttle comet | от 51 до 61% |
| Alpha Aurigids | 28 August – 5 September | 1 September | Auriga | Kiess comet (C/1911 N1) | 3% |
| South Taurids | 10 September – 20 November | 10-11 October | Taurus | Encke comet | 50-61% |
| Orionids | 2 October – 7 November | 21-22 October | Orion | Halley’s comet | 82-72% |
| Draconids | 6-10 October | 8-9 October | Draco | 21P/Giacobini–Zinner | 29-39% |
| North Taurids | 20 October – 10 December | 12-13 November | Taurus | 2P/Encke | 72-82% |
| Leonids | 6–30 November | 17-18 November | Leo | 55P/Tempel–Tuttle | 100-99% |
| Phoenicids | 28 November –9 December | 2 December | Phoenix | 289P/Blanpain (D/1819 W1) | 72% (view from Sydney, Australia) |
| Velida pupae | 1-15 December | 7 December | Puppis | Unknown | 35% (view from Sydney, Australia) |
| Andromedids | 1-8 December | 5 December | Pegasus/Andromeda | 3D/Biela comet | Unknown |
| Geminids | 4–20 December | 14-15 December | Gemini | 3200 Phaethon | 99-100% |
| Ursids | 17-26 December | 22-23 December | Ursa Minor | 8P/Tuttle comet | 61-51% |
What Is The Best Time To See The Meteor Shower In The UK In 2024?

Perseid meteor shower. Credit:almanac.com
Not all starfalls from this table will be visible to the UK residents. The population of the Northern Hemisphere will get their best chance to enjoy meteor showers from August 17 to 24, 2024.
What Is The Meteor Of August 2024?
The Perseid meteor shower from Comet Swift-Tuttle promises to be fast and very bright. At its peak, on August 12-13, you will have a chance to see up to 100 meteors per hour and even fireballs. The Moon, which will be in its first quarter phase during this period, explains such favourable observation conditions. When the aurora point reaches its maximum height, the Moon will disappear and will not interfere with observations. What time could we enjoy watching this meteor shower in the UK? From about midnight to 5 am. The Perseids are considered the best meteor shower in the Northern Hemisphere, as their peak occurs on warm summer nights.
It’s Showtime For Shooting Stars
Meteor showers are not a rare phenomenon, yet they are unforgettable for the observer. Keep an eye on the calendar, get ready to enjoy the spectacle that the Universe offers us. Don’t miss the next meteor shower of 2024! This is a show worth seeing at least once in your life.
References And Additional Information:
- Meteor shower calendar 2024: When to see a shooting star https://www.sciencefocus.com/space/when-is-the-next-meteor-shower-in-the-uk
- What Is a Meteor Shower? https://spaceplace.nasa.gov/meteor-shower/en/
- How to See Meteor Showers https://www.timeanddate.com/astronomy/meteor-shower/how-to-see.html
- Space and Astronomy Highlights in 2024 https://www.rmg.co.uk/stories/topics/space-astronomy-highlights-2024
![Beauty of the Pink Moon And Lyrid Meteor Shower in This Week’s Best Astrophotos [19-26 April] Beauty of the Pink Moon And Lyrid Meteor Shower in This Week’s Best Astrophotos [19-26 April]](https://orbitaltoday.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/Pink-Moon-is-on-its-way-above-the-mountains-1-300x300.jpg)
![Not Only Eclipse: Last Week In Best Astrophotos [5-12 April] Not Only Eclipse: Last Week In Best Astrophotos [5-12 April]](https://orbitaltoday.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/Veil-Nebula-300x205.jpg)




Thank you for your comment! It will be visible on the site after moderation.