Pioneers of the Red Planet: How Many Rovers are on Mars
13th Oct 2022
Colonizing Mars has become increasingly likely in recent years. But before you move into a new house, you must inspect it carefully. This is what Mars rovers do. So let’s look at how many rovers are on Mars, including for their history from the beginning until now.
Rovers on Mars: timeline
Since 1961, several dozen interplanetary automatic stations, including seven rovers, have been sent to Mars. The main advantage of rovers is that they can independently move around the planet’s surface and collect more data, while other spacecraft act as satellites in Martian orbit or as stationary descent probes. So, let’s discover all Mars rovers’ names.
How many Mars rovers have failed
The first step is always the hardest, and the first Soviet Mars 2 rover did not succeed. In general, the USSR was always in a hurry to be the first in everything, not caring much about the safety and practical benefits of its steps, so it often stumbled.
Mars 2 was the second of three automatic interplanetary stations (the Russian name for an uncrewed planetary space probe) from the M-71 series designed to explore Mars. On 27th November 1971, the station successfully entered the orbit of Mars and was supposed to deliver a landing module with a Prop-M rover weighing 4.5 kg. However, it crashed on the surface.
A Mars 3 attempt in December of the same year was more successful. The descent vehicle made a soft landing on the surface and even started transmitting data from it, but not for long — only 14.5 seconds, after which the connection was lost. This could have happened for two reasons: due to an extremely powerful Martian dust storm at the time or a problem with the orbiter’s ability to transmit messages. In 1974, the USSR made two more attempts to land the Mars 6 and 7 landers, but they did not even reach the surface.
By the way, the Prop-M vehicles could only be called Mars rovers with a stretch; in fact, they were physically tethered probes that were supposed to move on skis, being connected to the landing modules by cables. However, Mars 3 was the first spacecraft to touch the surface of the red planet, which is why we included it in our list.
How many rovers have been on Mars?
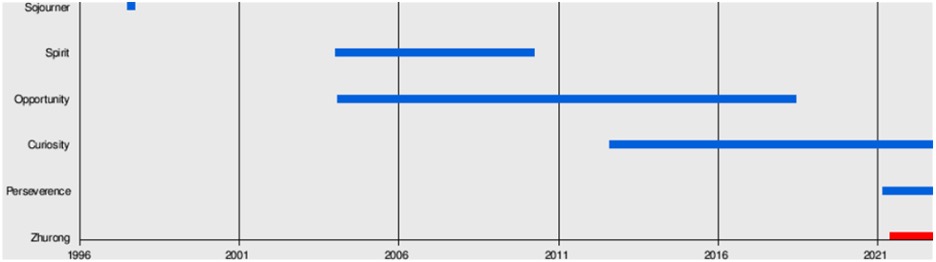
Since Mars 2, six rovers have visited Mars: five American spacecraft and a Chinese one. The Soviets’ example once again proved a lesson for NASA, and the agency decided to learn from others’ mistakes and take time to prepare for landing properly. The latter took almost 26 years.
Sojourner
The first NASA Mars rover, Sojourner, landed on the Red Planet on July 4, 1997. The mission was designed to validate new technologies (such as inflatable bags to cushion landings) and the concept of cheap scientific research (estimated at $428 million at current prices).
For this reason, a few instruments were installed on the 11.5-kilogram rover: a spectrometer, equipment for determining the degree of soil adhesion and abrasiveness, as well as a 3D mapping system for assessing the degree of danger for terrain movement, which included a pair of front cameras and a laser.
This was the first mission successfully completed by the rover: in total, Sojourner was able to work for 85 Earth days. Communication with the rover was interrupted due to the failure of electric batteries designed for one month of operation. The spacecraft managed to transfer 550 images and perform 15 rock analyses. Thanks to this mission, it was possible to determine the size of Mars’s metallic core in the range of 1300-2000 km.
Spirit
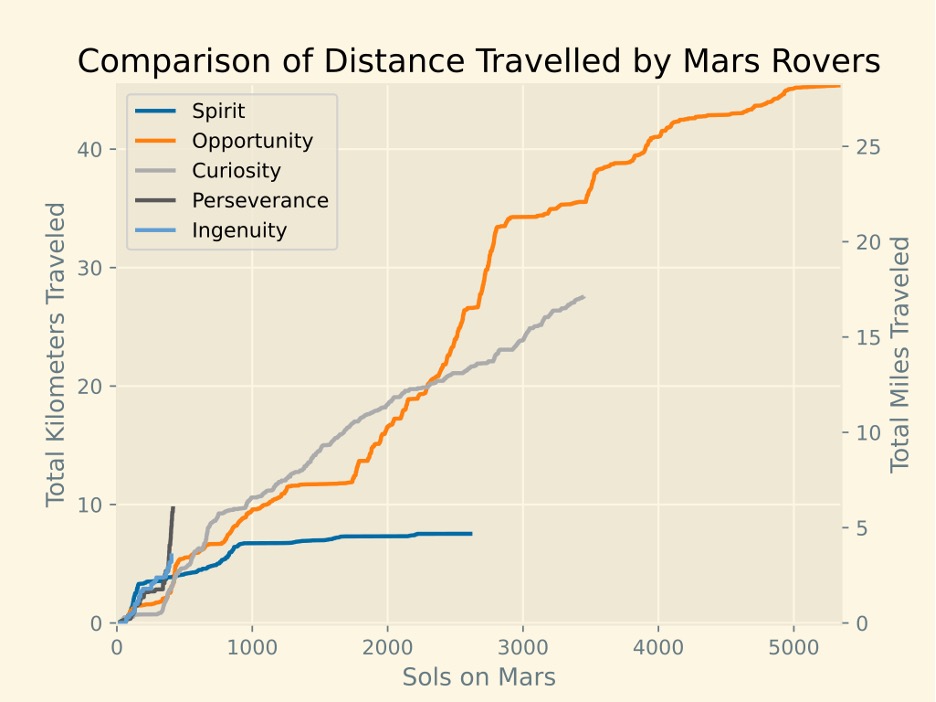
The Spirit rover landed on Mars on January 4, 2004. This device worked much longer than the planned 90 sols (Martian day). Thanks to the cleaning of the solar arrays by the natural Martian wind, power generation has increased significantly, which extended the spacecraft’s life. Spirit travelled almost 8 km instead of the planned 600 m, which allowed for a more extensive analysis of the Red Planet’s geological rocks.
After two years on Mars, Spirit’s front right wheel jammed, forcing the operators to drive it back to the front for the next four years — until it finally got stuck and froze from dusty batteries. However, this incident led to an unexpected discovery: silicate-rich soil became apparent in the furrow made by the dragging wheel. Efforts to free the rover did not stop until January 26, 2010; after that, it was used as a stationary platform, and communication with it was finally lost on March 22, 2010.
Opportunity
Three weeks after Spirit, its twin, Opportunity, landed in another region of Mars. Almost immediately after landing, both active Mars rovers managed to find hematite, and soon, Opportunity found deposits of sedimentary rocks on the crater walls. This discovery indicated the existence of a humid climate on Mars in the past. It also found a meteorite, which became the third similar discovery outside the Earth after the discovery of meteorites in the Apollo 12 and 15 missions (in the end, Opportunity managed to outdo the Apollo astronauts by finding three meteorites at once during its mission).
Opportunity surpassed the lifespan records of 5352 sols and covered a distance of 28.06 miles. The rover posted its last status on 10th June 2018, when a global Martian dust storm blocked out the sunlight needed to recharge its batteries. After hundreds of attempts to reactivate the rover, NASA declared the mission complete on 13th February 2019.
How many active rovers are on Mars
To date, the Red Planet is patrolled by three rovers — two from NASA and one from China. Lessons learned from the prior missions were taken into account while manufacturing these rovers, so they’ve managed to collect a lot more data than their predecessors.
Curiosity
This veteran rover landed on Mars on 6th August 6, 2012. During its stay on the planet, it managed to cover a distance of over 20 km. Curiosity’s discoveries include methane in the atmosphere, organic compounds in the soil, and clay deposits. In addition, the rover surveyed the slopes of Mount Sharp to study the geology and climate of Mars at various times.
Perseverance
Perseverance landed on the planet on 18th February 2021. Its purpose was to expand the knowledge obtained by Curiosity and search for convenient landing sites. In addition, Perseverance is equipped with the small Ingenuity helicopter, the first one to successfully fly into another planet’s atmosphere.
Zhurong
On May 15, 2021, the Chinese Zhurong rover landed on the surface of Mars, becoming the first non-American spacecraft to succeed. The purpose of its mission was to search for traces of life, as well as to study the surface of the planet and its environment.
The results of the Chinese rover operation made it possible to obtain topographic maps of the Martian surface indicating the characteristics of soils, the ionosphere, areas of water ice, and other scientific data. The estimated period of spacecraft operation, 90 Martian days, was exceeded several times!
On May 19, 2021, Zhurong sent the first images, and in June of the same year, a panoramic image from the landing site and a “group photo” of the rover and lander taken by a wireless camera were published.
Also, the researchers obtained a video with the sound emitted during the rover’s movement, and in July, the results of macro photography of Martian rocks were published. In addition, the spacecraft completed the study of two sand dunes, and on August 15, 2021, it successfully completed all the main stages of its scientific program. During this time, it transmitted over 10 gigabytes of data to Earth.
From mid-September to the end of October 2021, Zhurong was in a safe autonomous mode with limited power. The transition to autonomous mode was made because, during this period, the Sun came out on the exact line between Mars and Earth, making interplanetary radio communication almost impossible. For the same reason, other rovers on Mars (Curiosity and Perseverance) also went offline.
The graphs below show how much time all Mars rovers spent on the planet and how far they travelled.
Future rovers on Mars
The total number of rovers on Mars should increase soon, although the joint ExoMars mission of the European Space Agency and Roscosmos will not happen in 2022, as was planned before Russian aggression in Ukraine started. Probably, ESA will look for new partners. The project’s purpose is to search for traces of life and study Martian soil. The Rosalind Franklin rover is planned to be equipped with a 2 m drill to extract samples for the onboard exobiological mini-laboratory.
Japan also planned to send its MELOS (Mars Exploration of Life and Organism Search) rover in 2022 for an engineering demonstration of precise landing and search for possible biosignatures on Mars, but at the moment, JAXA does not report any updates regarding project implementation.
In the coming years, several Mars missions were planned by NASA and Roscosmos, but all of them were either cancelled for various reasons or transferred to orbital status without the need to land on the surface. It seems that Russia will now be out of space for a long time, and NASA is increasingly relying on SpaceX.
Elon Musk really has tangible plans for Mars. Back in the early 2010s, he announced plans on colonizing the Red Planet and is now confidently moving towards his goal. For this, a unique transport interplanetary system, Starship, is being built. Prototype testing is not always successful, but progress is evident. In the coming months, Starship will go on an orbital test flight. If it goes well, the next stop will be Mars. In 2024, the first cargo shuttles will go there, followed by the first colonists in 2028-2029. This, in turn, means that the number of rovers on Mars will soon increase. And while we are waiting for this grand event, let’s once again recall all names of rovers on Mars.
Mars rovers list
| Name | Status | Operation time | Discoveries |
| Mars 3, PrOP-M rover | NA | Landed on December 2, 1971. Mission failed. | ─ |
| Sojourner | NA | July 4, 1997 ─ September 27, 1997 | It had travelled a distance of just over 100 m (330 ft). Validation of new technologies (like inflatable bags to soften the landing) and the concept of cheap scientific research. |
| Spirit (MER-A) | NA | January 4, 2004 ─ March 22, 2010 | It had covered a distance of 7.73 km (4.80 mi). Worked much longer than planned 90 sols. Found hematite. |
| Opportunity (MER-B) | NA | January 25, 2004 ─ June 10, 2018 (last contact). NASA declared the mission complete on February 13, 2019. | Surpassed the previous records for longevity at 5,352 sols (5498 Earth days) and covered 45.16 km (28.06 mi). Found deposits of sedimentary rocks on one of the crater walls, which indicates the past existence of a humid climate on Mars |
| Curiosity (MSL) | Active | August 6, 2012 – present | Achieved more than all previous Mars rovers. Discovery of methane in the atmosphere, organic compounds in the soil, and clay deposits. Helped to discover that there was once water in Gale crater. |
| Perseverance | Active | February 18, 2021 ─ present Carried the Mars Helicopter Ingenuity. | Explored Jezero Lake crater. Provided sound recordings during landing and movement. Was the first one to convert carbon dioxide from the Martian atmosphere into oxygen. Successfully took 8 soil samples. |
| Zhurong | Active | May 22, 2021 ─ present | Transferred over 10 Gigabits of valuable information |
| ExoMars (Rosalind Franklin) | Planned | Postponed from September 2022 | __ |
| JAXA MELOS | Planned | 2022 | __ |
| SpaceX Starship Demo mission (Lander, Cargo) | Planned | 2024 | __ |





Thank you for your comment! It will be visible on the site after moderation.