China’s Xuntian space telescope launch delayed
22nd Nov 2023
In a surprise announcement, the National Astronomical Observatories of China announced that the launch of their upcoming Xuntian space telescope would be delayed until 2025. The telescope had been slated for launch by the end of 2023.
What is China’s Xuntian space telescope?
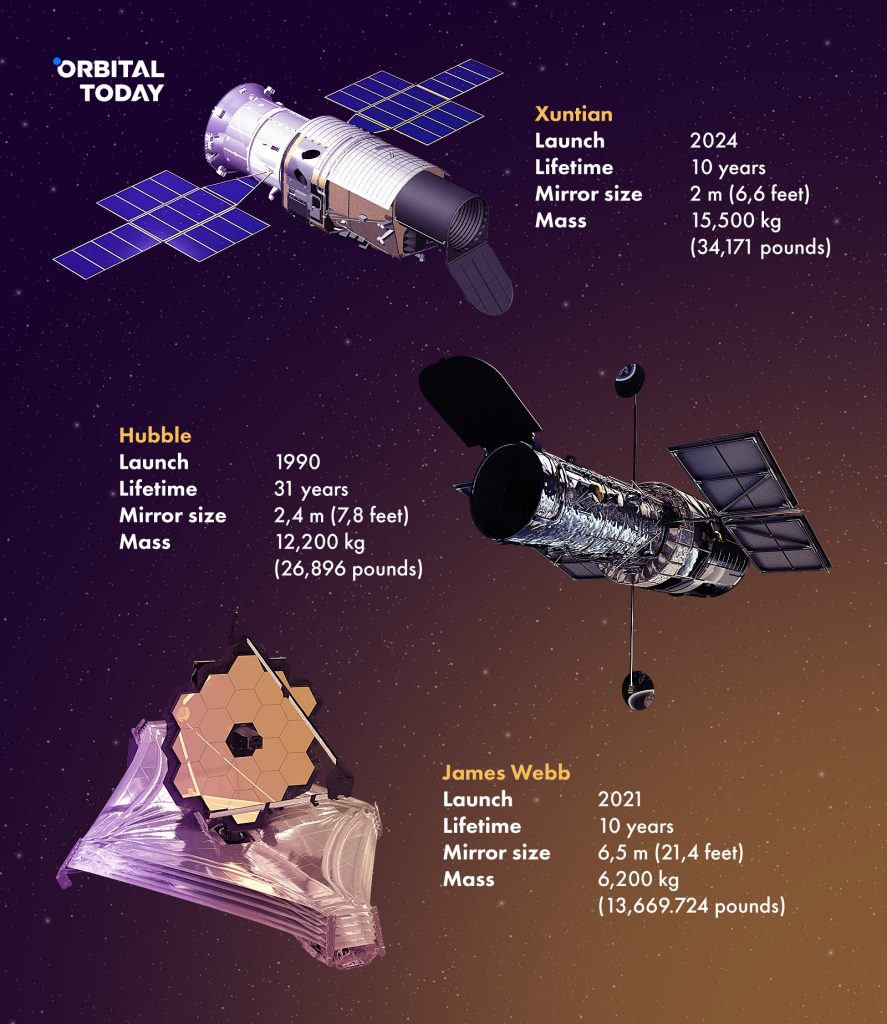
China’s space agency recently announced the launch of a space telescope that is expected to outperform NASA’s Hubble telescope. It will reach the size of a bus, weigh more than 10 tons and have a 6.6-foot diameter primary mirror. Thus, the new space telescope holds the honour of being China’s first large space telescope.
The Chinese survey space telescope (CSST) translates to ‘surveying the sky’ or ‘survey of the heavens’. Its primary mission is the exploration of dark matter, dark energy, and the universe’s evolution. To accomplish this, the Xuntian will have with a state-of-the-art 2.5-billion-pixel camera. Throughout its anticipated decade of activity, it will have the capability to survey approximately 40% of the celestial sphere.
In an interview on China Central Television (CCTV), Zhou Jianping, chief designer of the China-manned space program, praised the anticipated capabilities of the Xuntian telescope.
‘The Xuntian telescope marks a pivotal scientific endeavour, rivalling the significance of our nation’s space station program. It is a highly anticipated scientific asset for the Chinese astronomical community and symbolizes the nation’s top-tier technology in the field of astronomy,’ Zhou said.
Li Ran, project scientist of the CSST Scientific Data Reduction System, in an interview with China’s state-run Xinhua news agency, employed an analogy involving the imaging of a group of sheep to illustrate the Chinese telescope’s capabilities.
‘While Hubble might spot one sheep, the CSST can observe thousands, all with equal resolution,’ Li mentioned.
What are the goals and tasks of the Xuntian space telescope?
The primary goal of the CSST is to tackle fundamental questions about the universe. Some of its tasks that contribute to the development of global cosmological research include:
- Observing over one billion galaxies and measuring their positions which may help explain how those galaxies evolve
- Drawing a galactic dust map of the Milky Way
- Observing how super-massive blackholes are gobbling up surrounding materials
- Exploring exoplanets and discovering new peculiar celestial bodies.
Upon achieving orbit, this telescope holds the promise of:
- Offering breathtaking panoramas of the expansive Universe
- Unveiling concealed mysteries within our own solar system
- Extending its gaze deeper into the cosmos to witness celestial phenomena in neighbouring galaxies.
When is the launch of the Chinese survey space telescope?
The Chinese space telescope is poised to commence its scientific operations in 2024. The launch dates remain undisclosed.
The primary mission timeline of the Chinese space survey telescope spans ten years, with the option for potential extensions. As for today, the prototype sample is still in development. However, as Xu Shuyan, the chief designer of the Xuntian Optical Facility and Researcher from the National Astronomical Observatories of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, highlighted, creating all subsystems, components, and units is done. Now they are being getting ready for testing.
Xuntian vs. Hubble: Is CSST better than Hubble?
Today, the Hubble Space Telescope is hailed as NASA’s most exceptional achievement and a symbol of space exploration excellence. It can perform a wide range of astronomical observations: from monitoring celestial phenomena to probing dark matter and dark energy. It is considered to have no equals in high-resolution imaging and observing ultraviolet light.
However, Chinese astronomers confidently state that Xuntian will outperform NASA’s Hubble in its optical capabilities. They say that the technical characteristics of Xuntian will allow it to capture high-definition panoramic images of the universe with remarkable spatial precision. The Xuntian telescope from China boasts an extraordinarily vast field of view. This signifies the portion of the sky that a telescope can simultaneously observe. It will exceed Hubble’s capabilities by more than 300 times.
Furthermore, Xuntian has the potential to be a pivotal player in enhancing our comprehension of enigmatic dark matter and dark energy. By mapping the shapes and distribution of billions of galaxies, Xuntian aims to contribute valuable insights into fundamental cosmic mysteries. Additionally, its observations may complement the efforts of missions like Euclid, which dedicates to studying the nature of dark matter and dark energy. It may also contribute valuable insights into subjects like the birth of stars and the detection of exoplanets.
The debate over China’s telescope space potential to challenge Hubble continues.
Xuantian vs James Webb Telescope
Chinese astronomers have refrained from directly contrasting Xuntian with the James Webb telescope. On the contrary, the James Webb boasts a primary mirror measuring around 6.5 meters in diameter. Hubble’s mirror is substantially smaller, at 2.4 meters. The forthcoming Xuntian telescope from China will feature a two-meter diameter mirror, making it smaller than both the Webb and Hubble telescopes. Herewith, as NASA states, the James Webb Telescope’s field of view is fifteen times greater than that of Hubble. China’s Xuntian boasts a field of view over 300 times larger than Hubble.
On the contrary to NASA’s James Webb, Xuntian will be in a closer orbit to Earth. James Webb is situated approximately 1.5 million kilometres away at Lagrange Point 2, while CSST will orbit in proximity to China’s space station. This proximity reduces the challenges associated with servicing the telescope in comparison to telescopes located much farther away from Earth.
How will the Xuntian space telescope enhance China’s space station complex?
According to Chinese scientists, the Xuntian space telescope is intended to orbit in sync with China’s Tiangong space station, sharing the same path. This synchronized orbit will enable the Chinese telescope to operate independently and conduct continuous observations. This approach will enable Tiangong astronauts to make necessary upgrades when required.
Zhou Jianping anticipates that Xuntian will have a transformative impact on China’s national astronomical research efforts. He also expects it to enhance the value of the country’s space station complex.
“We expect the Xuntian space telescope to significantly accelerate the progress of astronomy, elevate China’s astronomical research to an internationally prominent position, and empower Chinese astronomers to become frontrunners in the field”, – he said.
Besides, launching Xuntian may become significant for cosmic research worldwide as well.
Is Xuntian Ready to Address Criticism and Skepticism Surrounding Its Capabilities?
Yet, there are doubts among some scientists about Xuntian’s capabilities. As it’s reported to have a larger field of view than Hubble but a smaller mirror. Potentially, this can lead to reduced collecting area and spatial resolution. In addition, it will have a lack of coverage in the far ultraviolet that ranges below 200 nanometres.
However, the scientific community eagerly anticipates China’s telescope’s potential contributions to humankind’s comprehension of the Universe regardless of its superiority to Hubble.
Nonetheless, scepticism looms among certain scientists in the space community regarding Xuntian’s capabilities compared to Hubble’s. While it boasts a larger field of view than Hubble, it comes with a smaller mirror. This may lead to diminished collecting area and spatial resolution. Its spectral resolution is reportedly lower than Hubble’s. It lacks the ability to observe wavelengths below 200 nanometers in the far-ultraviolet range.
The scientists remain hopeful about Xuntian’s potential contributions to our understanding of the universe, with both its reported advantages and limitations.






Thank you for your comment! It will be visible on the site after moderation.