Small but significant: How big is the Moon and why does it matter?
29th May 2023
More than half a century ago, a human foot touched the surface of the Moon for the first time. Since then, technological progress has come a long way, opening up more opportunities for us to explore the Moon’s surface. In 2019, NASA, in collaboration with the space agencies of Europe, Japan, and Canada, launched a new lunar program called Artemis, which involves not only the return but also the long stay of people on the Earth’s natural satellite. Why do we need this if it seems like all the mysteries of the Moon have been long solved?
The Moon will serve as the starting point for interplanetary travel, in particular, for flights to Mars, so the construction of a permanent base on the satellite is in the long-term plans. The implementation of the Artemis program has already begun; in the fall of 2022, the Orion unmanned spacecraft was successfully launched as part of its first stage. If all goes according to plan, after 2025 humanity will resume its moon walks.
There is more than meets the eye regarding Earth’s satellite. In this article, you will learn how big the Moon is compared to the Earth and other objects in the Solar system. It is bound to be interesting!
How big is our Moon?
The Moon is the closest celestial body to the Earth (approximately 384,400 km away), so it looks to us very large and bright. However, by cosmic standards, Moon’s size is quite modest. It is known that the ancient Greek astronomer Aristarchus of Samos was the first to try to establish the size of the Moon and the distance to it in the 3rd century BC. Later, a more successful attempt was made by Hipparchus of Nicaea, who, by observing the shadow of the Moon and using simple geometric techniques, determined that the radius of the Moon was 3.5 times less than the radius of the Earth. Then there was Galileo, who was the first to observe the Moon through a telescope and even make a map of its surface.
So what do we know about the size of the Moon today? Just like the Earth, it has a non-perfect spherical shape; therefore, its dimensions are determined based on the average value of the radius and go as follows:
- diameter – 3475 km;
- equator circumference – 10,917 km;
- area of Moon – 38 million km2.
Not much, isn’t it? By the way, do you want to know how long the Lunar Round Trip will take? Then read our article How Long Would It Take To Walk Around The Moon? You will find many interesting things there.
Is the Moon bigger than the Earth?
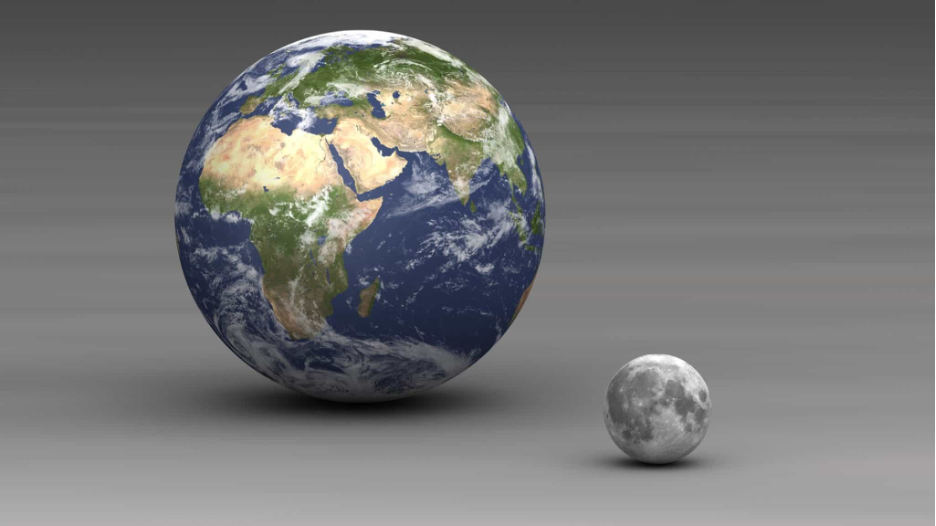

Certainly not. After all, the Moon is a satellite of the Earth, and the satellite is always smaller than its planet. How big is the Moon compared to the Earth? It is almost four times smaller.
The Earth’s dimensions are as follows:
- the average radius is approximately 6,371 km;
- diameter is 12,742 km;
- equator circumference – 40,075 km.
Simple mathematical calculations show us that the size of the Moon is only 27% of the Earth’s size. For clarity, if we imagine our planet as a nickel, the satellite will be the size of a coffee bean.
However, you may be surprised, but the Moon is the largest satellite in the “planet-satellite” system of our solar system. The ratio of the Earth and Moon masses is 81 to 1. No other planet has such large satellites.
How big is the Moon compared to a human, cities, countries
It is easier to understand the scale of the Moon if you know how much area some countries occupy. So, the USA, Europe, China, South Africa and Brazil could easily fit on the entire area of the satellite. There are more than 24 thousand cities like London and more than 7.5 billion football fields!
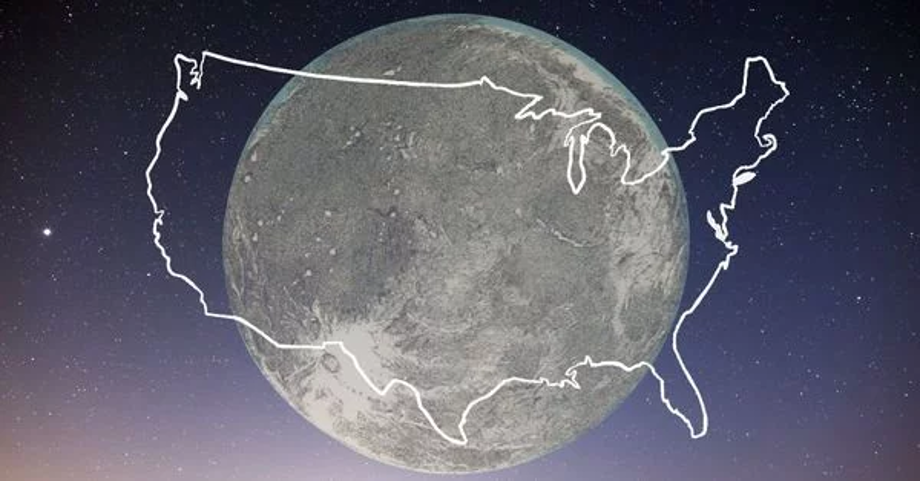
And how big is the Moon compared to us? As we remember, the Moon’s surface area is about 38 million square kilometres. If everyone on the Moon were standing or sitting, taking up about 1 square metre each, you’d fit 38 billion people. It is five and a half times more than the population of Earth, which is four times the size of the Moon! For comparison, the most populous country on Earth is Bangladesh — with 1140 people per square kilometre. Fortunately, overpopulation is no threat to the Moon. Even when, over time, a base for astronauts is built there, no more than a few dozen people will stay on it.
What does comparing the Earth and the Moon give us?
Moon size has a direct impact on many processes occurring on Earth. The satellite’s gravitational field affects the Earth’s biosphere and causes, in particular, changes in the Earth’s magnetic field. The rhythm of the Moon affects the tides and air pressure, causes changes in temperature, wind actions, and also influences water levels.
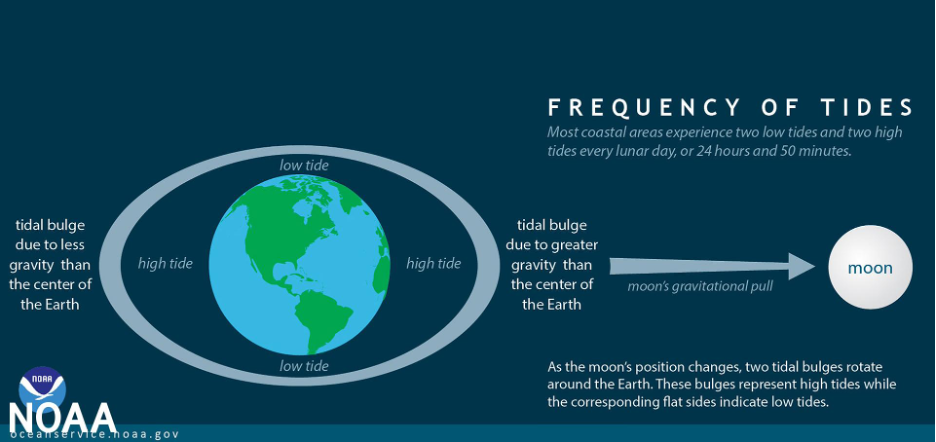
Planetologists believe that it is the Moon that contributes to the stabilization of the Earth’s orbit, as well as the tilt of the axis of rotation, which, in turn, affects the formation of the seasons. If the Moon were to suddenly shrink or disappear altogether as if in some science fiction movie, it would cause extreme climate change, the poles would become hot, the equator would freeze, the tides and seasons would be a thing of the past, and the ecosystem would break down. Fortunately, this scenario will not threaten us for a very long time. The Moon moves away from the Earth every year by only 3 cm, and it will take more than one million years for it to leave the Earth’s orbit.
How big are Mars and other planets compared to the Moon?
So, we found out that it is four times smaller than the Earth, whereas the Earth is the largest among the terrestrial planets but only the fifth in diameter and mass among all the solar system planets. How small is the Moon compared to other planets?
Venus resembles the Earth in size, so the parameters will not differ much — by about 1.5-2%. But if we compare the size of the Moon with the smallest planet, Mercury, then it will be 71% of Mercury’s size.
No less interesting is the result of comparing Moon and Mars. We know that Mars is about two times smaller than Earth; therefore, Moon is half the size of Mars. The radius of Mars is 3390 km, and the radius of Moon is 1737 km, so the ratio of the Moon to Mars is 51.23%. It is hard to imagine the force of gravity if a satellite the size of half our planet revolved around the Earth.
The ratio of the size of the Moon and the largest planet — Jupiter (radius 69,911 km), is only 2.5. But then how large are Jupiter’s moons? Bigger than ours or not?
How big is the Moon compared to other moons?
Jupiter has the largest moon in the solar system. This is Ganymede, with a radius of 2,631 km. The satellites Callisto and Io with radii of 2410.3 km and 1821.6 km are also larger than our Moon. But! The sizes of Jupiter’s moons are only 3.8%, 3.4%, and 2.6% of the parent planet’s size. Saturn has a similar situation with the second-largest satellite in the solar system — the radius of Titan is 2575 km, which is 4.4% of the size of the main planet.
As we can see, the Moon is the 5th largest satellite in the solar system, but in relation to its planet, it is the first.
How big is Pluto compared to the Moon?
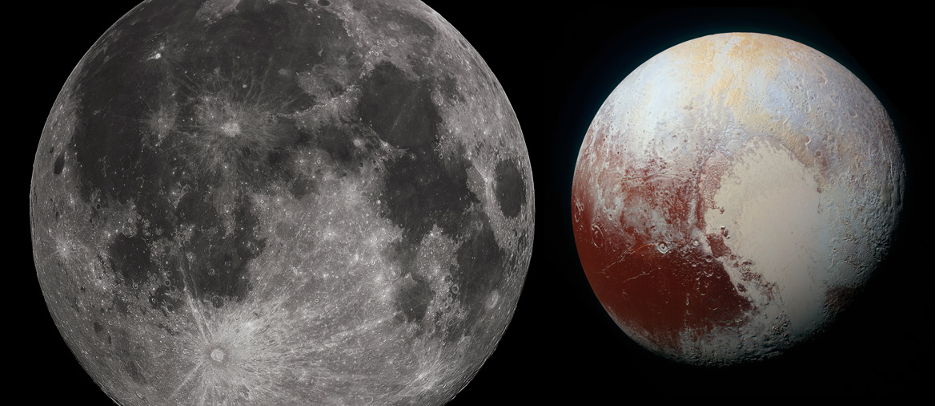

Until 2006, the solar system included nine planets. And if the 9th planet, Pluto, with a radius of 1188 km, had not been excluded and transferred to the category of dwarf planets, then the Moon would have surpassed it in all respects:
- over six times larger in mass;
- three times larger in volume;
- 6% larger in size.
But in the satellite/planet system, the Moon would yield to Pluto’s satellite Charon because its size is 51% of the size of Pluto.
Why does the Moon seem small and then big?
Sometimes the Moon seems suspiciously huge to us, but we understand that its size is stable, and certainly cannot decrease or increase from time to time. Then why does it seem to change in the sky? The answer is in the Moon’s orbit. The lunar orbit is an ellipse, so, at different times, the satellite is at different distances from the Earth. The Moon appears smaller when it is at its apogee, the farthest point of the ellipse at a distance of about 406,000 km. Still, when it is at perigee (about 363,300 km) and if the full moon occurs during this period, the supermoon effect follows.
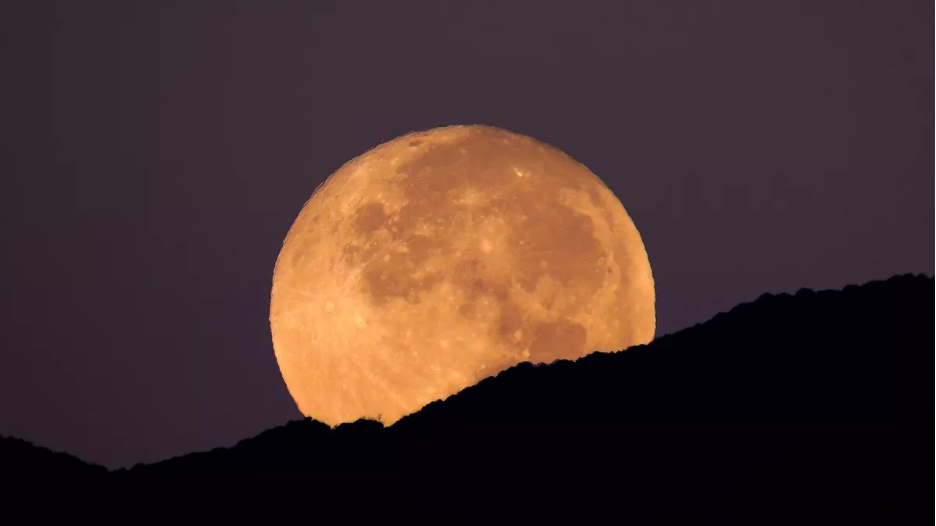

How do we see Moon during its supermoon period? We see the satellite 14% larger and 30% brighter than on other days, despite possible cloud cover. We can see the huge Moon once every 414 days.
Conclusion
Scientists have long figured out how big is the Moon, and how its size affects Earth. This decade could be a milestone in space exploration — once again, thanks to the Moon. The return to the satellite promises to bring the Mars mission closer. Let a new era of space exploration begin!





Thank you for your comment! It will be visible on the site after moderation.