The Armageddon Scenario: Will an asteroid hit Earth and what aftermath can we expect?
31st Jul 2022
A giant asteroid is rushing toward the Earth, and the best scientists and military men in the world are looking for a solution to save our planet and humanity itself! This reminds you of a plot from a famous Hollywood movie, doesn’t it? Luckily, everything ends well in the movie. But can such a scenario become a terrifying reality? Will an asteroid hit Earth, and can we protect ourselves from this global catastrophe? Let’s find out.
What are asteroids, and how big are they?
Scientists describe asteroids as “rocky celestial bodies smaller than planets that revolve around the sun”. Most (about 75%) consist of carbon and silicon, while the rest are iron and nickel.
The largest cluster of asteroids in the solar system is the main asteroid belt between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter. Over 200 asteroids with a diameter of more than 100 km circulate in the belt, along with 1.1-1.9 million with a diameter of more than 1 km and millions of smaller asteroids. In addition, there is also the Kuiper belt at the edge of the solar system near Neptune, the Hilda family behind the main belt, and clusters of “Trojans” and “Greeks” at Lagrange points.
Ceres was considered the largest asteroid in the solar system, reaching almost 1000 km in diameter, but on August 24, 2006, it was given the status of a dwarf planet. The other two largest asteroids, Pallas and Vesta, have a diameter of about 500 km, and the fourth on the list of giants, Hygeia, is 430 km.
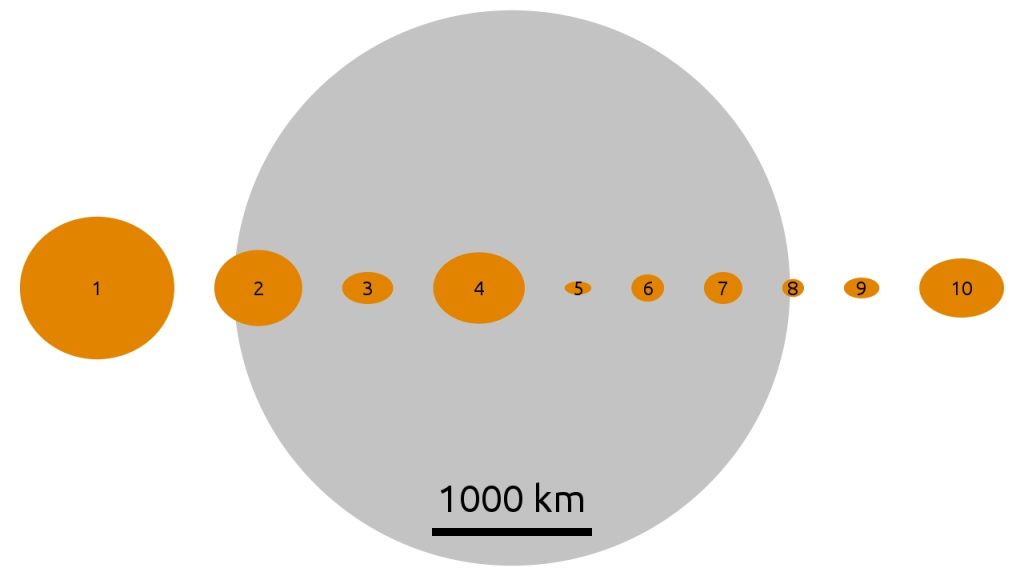
And this is what the first ten asteroids look like on the scale of the Moon, the diameter of which is only 4 times smaller than the diameter of the Earth. The objects, left to right, are:
- Dwarf planet Ceres,
- Pallas,
- Juno,
- Vesta,
- Astraea,
- Hebe,
- Iris,
- Flora,
- Metis,
- Hygiea.
How likely is an asteroid to hit Earth?
Very likely. Moreover, according to NASA, about 20 asteroids fall to Earth every day. Fortunately, these are mostly small bodies ranging from a few centimeters to several meters in size, which burn up in the atmosphere and do not pose any danger to us. Because of the bright trail, they leave in the sky, they are also called meteors.
On October 7, 2008, the 2008 TZ3 meteorite fell to Earth in the Sudan region. TZ3 measured from 2 to 5 meters. Entering the Earth’s atmosphere at a speed of 27 thousand miles/hour, it began to collapse at an altitude of 46-42 km and exploded at an altitude of 37 km. Only 0.005% of the TZ3’s original mass was collected on the surface; the rest burned up in the atmosphere.
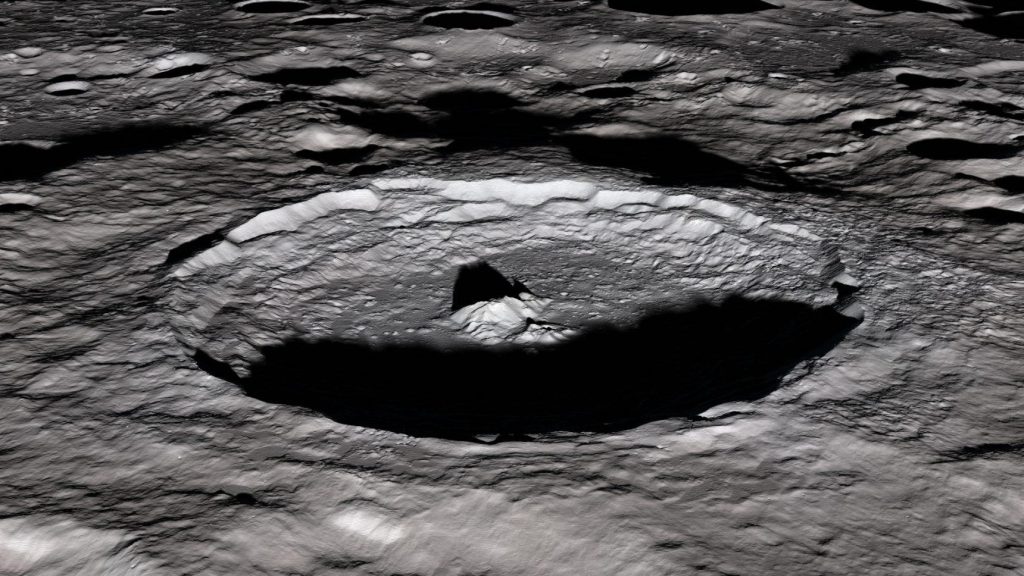
But the Moon is less fortunate. Due to the lack of atmosphere, soil, and water bodies, all traces of asteroid impacts are visible at a glance. That is why the entire lunar surface is dotted with craters.

How big of an asteroid would destroy Earth?
A celestial body capable of causing a global catastrophe by colliding with the Earth would have to be at least a kilometer in diameter. But such a meteor strike occurs extremely rarely, about once every 100,000 – 500,000 years.
Has a very big meteorite ever hit earth? Well, what do you think killed the dinosaurs? 65 million years ago, a huge asteroid fell on the territory of modern Mexico, forming a crater with a diameter of 180 km! This catastrophe led to the extinction of 50% of the biota and a decrease in global temperature of 7-8 degrees. As a result, those heat-loving lizards gradually disappeared from the face of the planet.
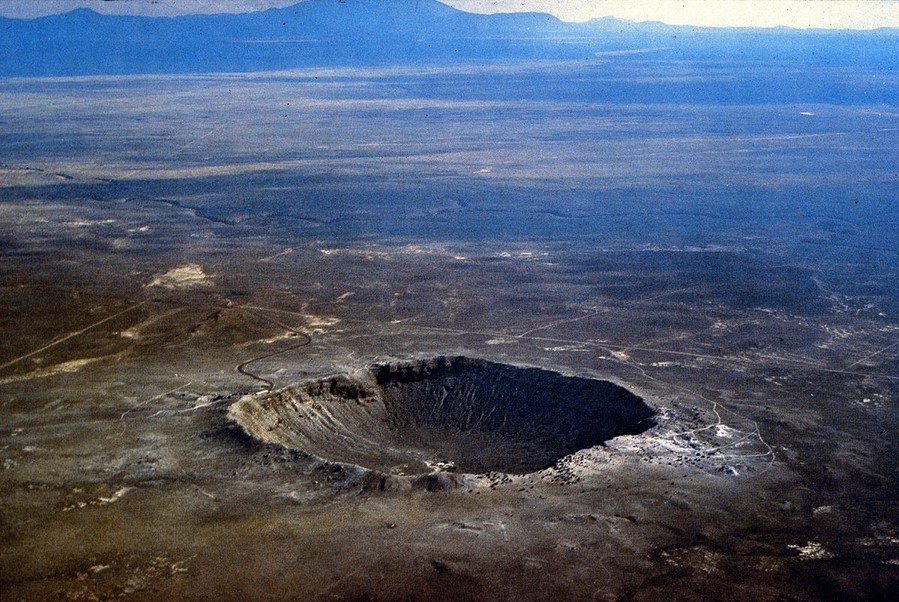
The Arizona crater in the United States is more recent evidence of a large asteroid colliding with Earth. Its diameter is 1219 meters, and its depth is 229 meters. According to experts, the crater arose about 50 thousand years ago, after the fall of a 50-meter asteroid weighing 300,000 tons.

Is there an asteroid heading towards earth now? Yes, and more than one. From time to time, relatively large meteorites approach the Earth. This poses a potential threat, but fortunately, the collision does not happen, and dangerous guests fly by.
Will an asteroid hit Earth in 2022?
A question that troubles many people: Will an asteroid hit Earth in 2022? No. We have been lucky so far. In May 2022, NASA announced the approach of asteroid 1989 JA. This was a stone four times the width of the Empire State Building and it flew by at a distance of 2.5-million-miles from Earth. The distance may seem huge, but on a cosmic scale, it is regarded as potentially dangerous since the speed at which the object is moving is enormous (about 30,000 miles/hour), and any change in its trajectory could have reduced the distance in a matter of hours.
But what will happen if Earth is hit by an asteroid?
Modern history, fortunately, knows only one fact of a serious collision of an asteroid with the Earth. On June 30, 1908, a 120-foot object of unknown origin fell into the region of the Tunguska River in Siberia. The explosion was so strong that it was heard 800 km from the epicenter and caused a magnetic storm that lasted 5 hours. The blast knocked down the forest in an area the size of London, shattered windows in houses within a radius of 200 km, and an intense glow of the night sky and luminous clouds were observed until the end of August.
According to scientists, the power of the explosion caused by the Tunguska meteorite fall was 10-15 megatons of TNT, which corresponds to the energy of an average hydrogen bomb. If Tunguska had fallen on a big city, no trace would have been left of it.
When is the next asteroid predicted to hit the earth?
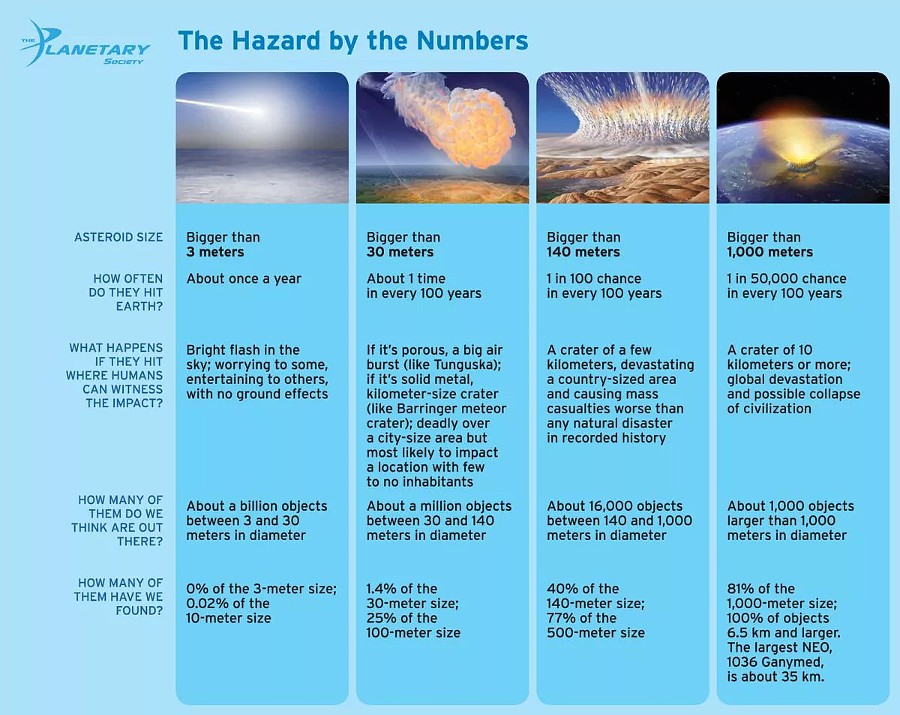
Scientists’ approximate calculations show that the probable frequency of meteorites like Tunguska falling to Earth occurs every 100 years. Regarding other meteorite sizes, here the dependence is simple: the larger, the less often, and vice versa. There is no upper limit on the extent of possible damage, while the development of scientific and technological progress (getting into nuclear power plants, for example) and overcrowding only increase the risks.
In the picture below, you can see what hazards asteroids of different sizes carry and how often you can expect a collision with them.
What asteroid will almost hit Earth?
According to NASA’s estimates, in 7 years, on April 13, 2029, the “potentially dangerous asteroid” Apophis, discovered in 2004 and named after the ancient Egyptian personification of evil, a snake that lives in darkness and tries to devour the sun god Ra, will approach the Earth. The celestial body will pass within the orbits of our geostationary satellites at a distance of only 19,000 miles from the Earth’s surface! And this is very close for such a giant as Apophis. Its diameter is about 1100 feet, almost ten times the size of Tunguska.
The passage of Apophis will be so bright that about 2 billion people will be able to see it with the naked eye. First, like a bright star stretching across the sky from east to west, it will fly over Australia, then over the Indian Ocean, and, finally, cross the equator over Africa.
So will an asteroid hit earth in 2029?
No. The calculations show that the probability of a collision of the asteroid Apophis with the Earth is zero. So far, we’re safe. However, Apophis will approach the Earth not only in 2029, but also in 2036 and 2068. And who knows how it will behave then.
But if it does hit us, can you survive an asteroid?
Everything will depend on the celestial body size, but the chances of survival will increase significantly if we try to prevent a collision. Modern satellite systems and telescopes Sentinel, Hubble, JWST, and others help us monitor the starry sky and track potential threats.
Do we have an asteroid defense system?
But does Earth has an asteroid defense system? There is no fully developed operating system yet, but here is what NASA, other space agencies, and research centers offer.
DART
Double Asteroid Redirection Test Mission uses ultra-high-speed spacecraft technology. Эта anti-asteroid defense system relies on a kinetic impact on the asteroid, which should change its flight trajectory.
The DART mission was launched on November 23, 2021, by NASA together with SpaceX. DART makes a one-way flight to the Didymos asteroid system. The DART target is Dimorphos, which is approximately 530 feet in diameter.
Can Dimorphos hit earth? No. But the test will provide scientists with important data to help prepare for a real collision in the future. The spacecraft will crash into Dimorphos sometime in the fall of 2022 at a speed of approximately 4 miles per second. Scientists estimate that the kinetic impact will shorten Dimorphos’ orbit by several minutes. Researchers will accurately measure this change using various telescope types on Earth. The results will make it possible to determine the effectiveness of the kinetic impact as a reliable method for deflecting an asteroid.
Nuclear impactors
Another potential type of anti-asteroid defense systems. In fact, this is the same DART, but instead of a ship, nuclear charges are used. Note that this tech is not about exploding an asteroid, as we could see in the Armageddon movie, but about the impact. The explosion was rejected by NASA as a method contradicting common sense. After all, splitting the asteroid would create many smaller, but no less dangerous, fragments. Changing the trajectory method eliminates this problem.
Laser beams
The third anti-asteroid defense system worth noting is the DE-STAR asteroid defense system, developed by the UCSB Experimental Cosmology Group under the auspices of NASA/ESA. The project implies the development of two types of lasers: a large one that will be placed in Earth’s orbit and destroy asteroids at close range, and a small one that will be sent to the target on a spacecraft. In addition, the system will be able to perform a number of auxiliary functions:
- space debris removal,
- power supply and recharging of remote objects,
- remote photon movement of small space vehicles.
Laser Bees
Yes, you read it right. The method is based on the same concept as the one described above, except that the lasers are fired by tiny robotic objects. The planetary society, which recently launched Solar Sail, is working on the idea and the universities of Strathclyde and Glasgow.
Gravity tractor
Last but not least anti-asteroid defense system. This technology operates on the principle of capturing a celestial body in its gravitational field, thus affecting its trajectory. The concept was first voiced in 2005, however, it is so difficult to implement at the level of today’s technologies that it cannot be achieved without an engineering feat.
Fortunately, we are unlikely to need to use such technologies in the near future. Scientists unanimously answer the question, will an asteroid hit earth in 2022, 2023, and at least the next 20-30 years, in the negative. But everything can change at any moment, and it’s better to be prepared so as not to repeat the fate of the dinosaurs.






Thank you for your comment! It will be visible on the site after moderation.