New Player is Getting Ready: Astra Launch History (Updated)
19th Apr 2022
Astra Space is a California-based private aerospace company that specialises in providing fast and cheap access to space in the small payload orbital launch niche, however Astra’s launch history has not always been smooth. Astra Space was founded in 2005 as Ventions LLC and initially worked on the miniaturisation of rocket engine technology in partnership with NASA and DARPA. In 2016, it was reorganised into Astra Space Inc. and changed the focus of activities to the creation of small-lift launch vehicles with a payload capacity of up to 200 kg.
The founders of Astra Space, former NASA IT director Chris Kemp and PhD space engineer Adam London, say they want to create a space analogue of the logistics giant FedEx to massively and affordably send microsatellites and CubeSats to LEO on their rockets. According to Kemp, in the next few years, Astra Space will launch payloads to any place in space, on any schedule, from anywhere on Earth.
Astra rocket compared to Rocket Lab, Virgin Orbit and SpaceX
Here’s what the Astra Rocket’s main specs look like compared to the international competition.
| Rocket | Payload, kg | Launch Cost, million $ | Height, m |
| Space X Falcon 9 | up to 22 800 | 52-62 | 70 |
| Virgin Orbit Launcher One | 300-500 | 12 | 21 |
| Rocket Lab Electron | 150-225 | 6.5 | 17 |
| Astra Space Rocket 3 | 75-205 | 2.5 | 12 |
What benefits can launching with Astra Space bring?
The unprecedented low cost, high mobility and efficiency of Astra Space launch, according to the company CEOs, can really revolutionise the market. The rocket and the entire launch infrastructure can fit in standard shipping containers, allowing for quick delivery up to 24-hours readiness. This makes launching rockets with Astra especially attractive for the military – for example, if necessary, you can start urgent monitoring of a certain territory.
In mid-2020, Astra Space entered into a military contract with the U.S. Space Force for two commercial launches. The total amount of the Astra Space launch contracts is about $150 million (more than 50 launches), and half of its clients are governments of different countries.
In many ways, Astra owes such demand to the speed of its progress. For comparison, it took SpaceX 7 years to develop and launch a rocket into space, Rocket Lab – 12 years, Virgin Orbit‘s Launcher 1 – 13 years, and Astra – only 5 years. In just five years, Astra Space has gone through a full cycle from the development of a carrier to its launch. Three modifications of the Astra rocket were created and tested; however, such an intense pace had its consequences.
Out of 8 Astra launches since 2018, including test ones, only one rocket launch was fully successful. However, Chris Kemp and Adam London consider this to be a normal workflow. They are looking to the future with confidence and getting ready for Astra’s next launch. The company’s shares price is increasing, and Astra Space’s ideas do not dry out. Improved Rocket 4 and Rocket 5 are already being developed and getting ready for Astra Space’s next launch. The Rocket 5 is intended for the rapid delivery of goods via sub orbit from one point on the globe to another. That is, Astra is considering a strategy to enter not only the orbital market but also suborbital launches.
If these grand plans become a reality, the leading micro-launchers Rocket Lab and Virgin Orbit will gain a serious competitor as Astra Space progresses. After all, Astra’s rocket launch is many times cheaper, and the launch itself does not require long preparation. There is only one thing left – to increase carrier reliability. After all, the track record of Astra launches is red with failure so far.
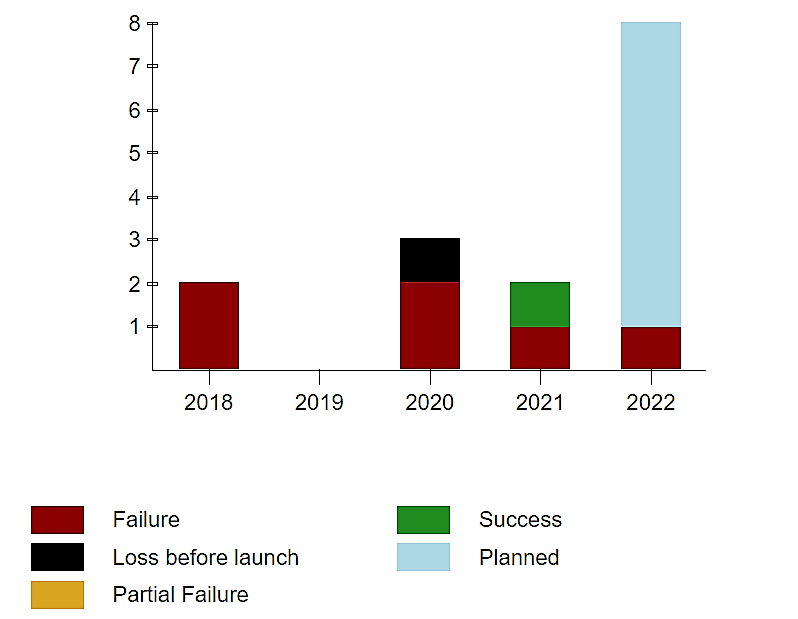
Astra rocket launch schedule
Below is the Astra launch schedule starting from the very first launch. We will add to the list of events, so we suggest you bookmark this page if you want to stay updated on each new Astra launch date.
|
# |
Date |
Rocket Gen |
Payload |
Customer |
Orbit |
Launch Site |
Result |
|
1 |
20.07.2018 |
1 |
Mass simulator |
Test Flight |
Sub |
Kodiak Launch Complex, Alaska |
Unknown Failure |
|
2 |
29.11. 2018 |
2 |
Mass simulator |
Test Flight |
Sub |
Kodiak Launch Complex, Alaska |
Failure (engine breakdown) |
|
3 |
23.03.2020 |
3.0 |
Unknown |
DARPA |
LEO |
Kodiak Launch Complex, Alaska |
precluded |
|
Mission failed to launch within the challenge’s launch window due to an issue with a sensor for the guidance, navigation, and control systems. The rocket was reused for the next launch without DARPA involvement, but on 23 March 2020, a fire occurred on the launch pad prior to launch, destroying the rocket |
|||||||
|
4 |
12.09.2020 |
3.1 |
None |
None |
LEO |
Kodiak Launch Complex, Alaska |
Failure |
|
Second attempt to launch a Rocket 3 for the first time. Initially intended to be the second of two launches for the DARPA Launch Challenge. 30 seconds after lift off range safety officer shut down engines |
|||||||
|
5 |
15.12.2020 |
3.2 |
None |
None |
LEO |
Kodiak Launch Complex, Alaska |
Partial success |
|
First time then Astra rocket could reach its target orbital altitude of 390 kilometers but failed to reach stable orbit due to issues with the upper stage propellant mixture ratio. |
|||||||
|
6 |
28.08.2021 |
3.3/LV0006 |
STP-27AD1 |
US Space Force |
LEO |
Kodiak |
Failure |
|
First commercial Rocket 3 demonstration launch for the U.S. Space Force. An engine failure shortly after liftoff caused the rocket to drift sideways off the launch pad before ascending vertically. Range safety ordered engine shutdown, terminating the flight. A fueling system propellant leak was determined to be the root cause of the problem. |
|||||||
|
7 |
20.11.2021 |
3.3/LV0007 |
STP-27AD2 |
US Space Force |
LEO |
Kodiak |
Success |
|
8 |
10.02.2022 |
3.3/LV0008 |
BAMA-1, INCA, QubeSat, R5-S1 |
NASA |
LEO |
Cape Canaveral |
Failure |
|
The ELaNa 41 mission, consisting of four CubeSats, was launched on this flight. An issue occurred after stage separation during flight which prevented delivery of the payloads into orbit. |
|||||||
As you can see, Astra rocket launch failures do not bother Astra Team too much. The next launch of Astra Space should have taken place on 20th February. Rocket 3.3 was trying to bring the S4 Crossover base payload platform prototype from NearSpace Launch to SSO.
Who never climbed never fell
However, difficulties do not stop Astra Team. After the third unsuccessful Rocket 3.3 Launch on February 10, 2022, the company conducted a thorough investigation into the causes of the accident that resulted in losing the payload and the rocket; 35 days later, Astra rehabilitated itself by carrying out a flawless mission.
The latest Astra Space Launch
On March 15, 2022, at 16:22 UTC, Rocket 3.3 lifted off from the Kodiak Space Center in Alaska with a rideshare mission for Spaceflight, Inc. All payloads deployed successfully to SSO. The main payload – S4 Crossover, carrying EyeStar-S4, remained attached to the second stage as intended.
Three minutes after liftoff, the five LOX/Kerosene-fueled Delphin first-stage engines shut down, and fairing separation began. This moment was very important for Astra Space because, during the previous launch, the problem that led to a crash occurred at this particular stage.
The fairing protects the payload and the upper stage during atmospheric flight and makes the second stage’s construction lighter and simpler. Its separation is necessary for the deployment of satellites and the separation of the second stage since it is also shielded by a fairing.
Once the LV0009 fairing separation sequence was completed, the second stage separated and ignited its only engine, also using LOX/Kerosene. Ten seconds after the second-stage engine was switched off, the sequential payload deployment began. Besides, the satellites left the tracking zone of ground telemetry stations for some time, and the Mission Control Center could not immediately confirm payload separation. However, when the satellites returned to the visible zone, the mission’s success was confirmed. The mission was given an unofficial title of Unexpectedly Successful.
Watch the video of the last Astra launch to see how it went
So, the Astra seems to be coming out of the doldrums. We wish the company good luck in the next three NASA Tropics missions scheduled for June, and of course, we will definitely keep you posted on all new developments!
Follow our updates!






Thank you for your comment! It will be visible on the site after moderation.